Cytokine Storm and Laboratory TestingEducational Resources for you
Essa informação foi útil?
†ADVIA Centaur IL6 assay has been authorized by FDA under an EUA for use by authorized laboratories. This test has been authorized only to assist in identifying severe inflammatory response, when used as an aid in determining the risk of intubation with mechanical ventilation in confirmed COVID-19 patients. This test is only authorized for the duration of the declaration that circumstances exist justifying the authorization of emergency use of in vitro diagnostics for detection and/or diagnosis of COVID-19 under Section 564(b)(1) of the Act, 21. U.S.C. § 360bbb-3(b)(1), unless the authorization is terminated or revoked sooner. Product availability may vary from country to country and is subject to varying regulatory requirements. Please contact your local representative for availability.
‡ Product availability varies by country.
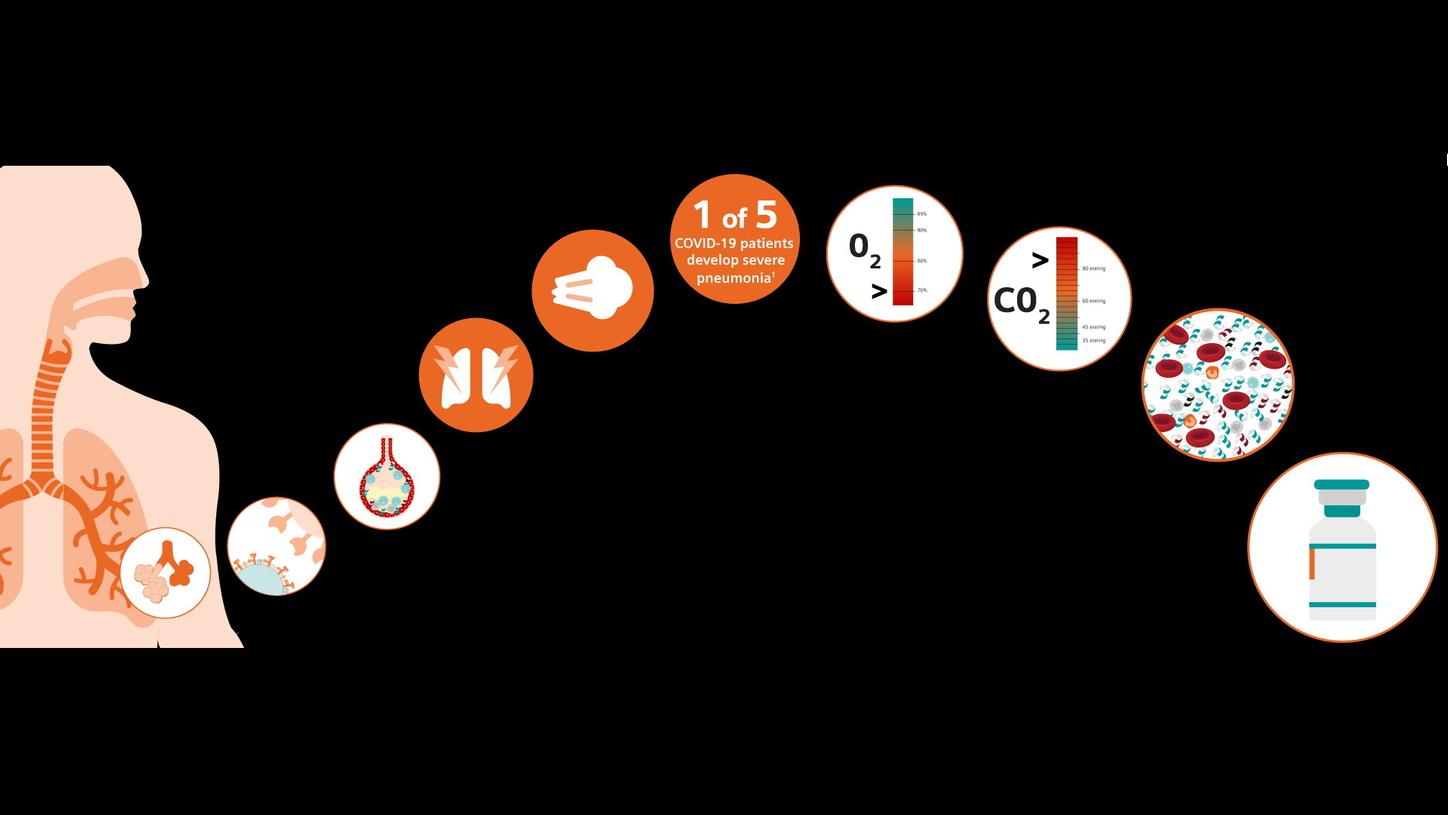
1 Siddiqi HK, et al. J Heart Lung Transplant. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.healun.2020.03.012.
2 Zhou Y, et al. National Science Review. 2020. DOI: 10.1093/nsr/nwaa041.
3 Qin C, et al. Clin Infect Dis. 2020. https://academic.oup.com/cid/advance-article/doi/10.1093/cid/ciaa248/5803306.
4 Del Valle, Kim-Schulze, Huang, et al. https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.05.28.20115758.
5 Zhou F, et al. The Lancet. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30566-3.
6 https://www.ifcc.org/ifcc-news/2020-03-26-ifcc-information-guide-on-covid-19/. (Accessed January 5, 2021).
IMMULITE TNFα, IL-1ß, IL2R, IL-6, IL-8, and IL-10, Atellica IM IL- 6, BN and Atellica NEPH SAA assays are not FDA cleared/approved for sale in the U.S.
Some or all uses of the analytes described have not been approved or cleared by the FDA.