- Home
- Medical Imaging
- Ultrasound Machines
- Meet the DAX
Meet the DAXTaking ultrasound to new depths
Clinical Trends

Prevalence of obesity among adults is making medical diagnoses difficult
Radiology departments are challenged by the prevalence of obesity and the increased utilization of bariatric surgical techniques, with ultrasound being the most highly impacted imaging modality.

Obesity’s negative impact on the quality of treatment
Since the amount of tissue on a patient’s body can negatively impact the quality of the soundwaves and subsequent image coming from the scanner, it is estimated that obese patients are 1.65x more likely than others to have significant undiagnosed medical conditions2 and nearly 50% of all cancer patients younger than 65 were associated as overweight and obese.3
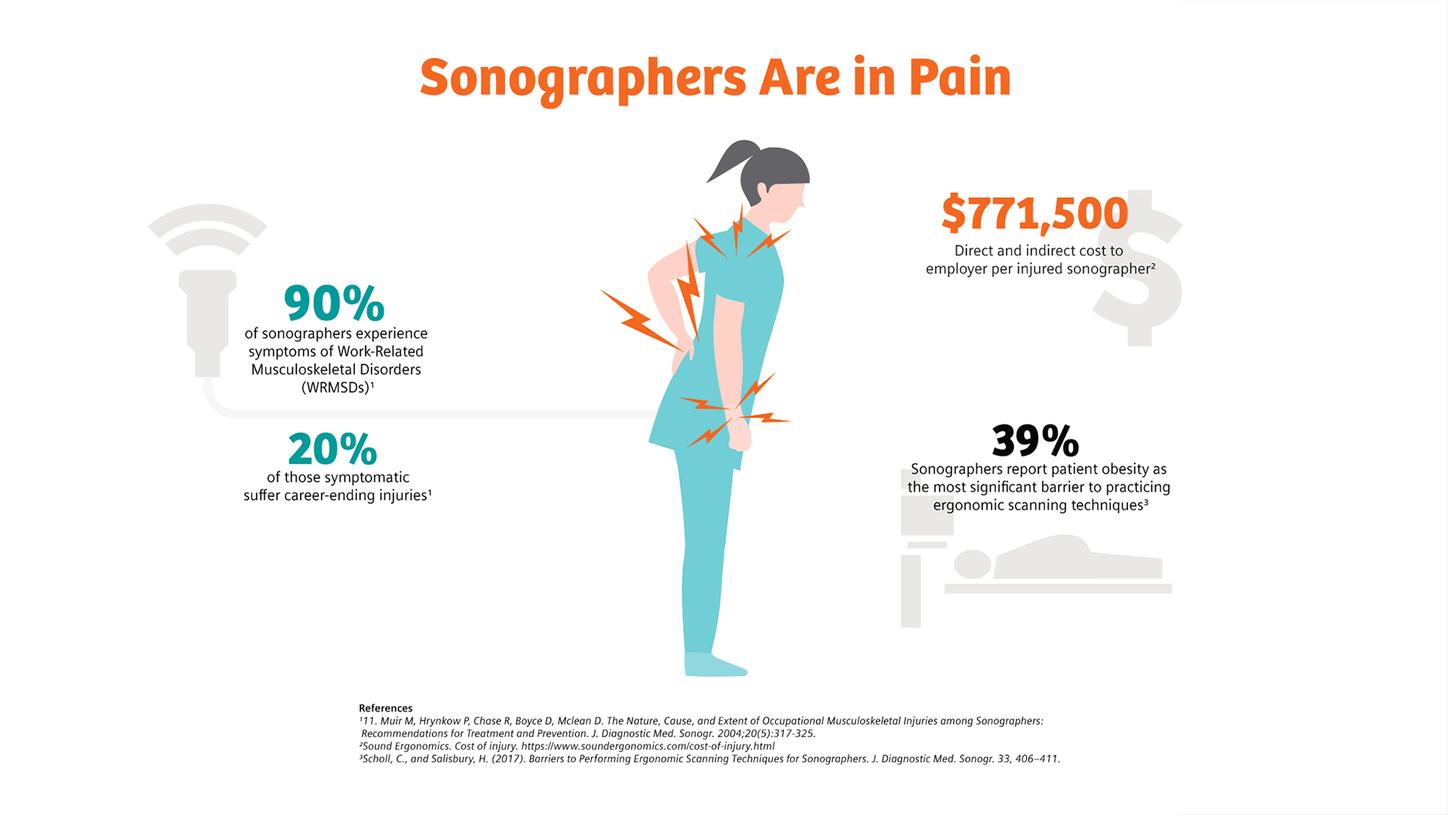




Barriers to performing ergonomic scanning techniques for sonographers
Obese patients often require excessive pressure that can result in overexertion of the upper extremity.
As a result of the excessive pressure that is often required to image bariatric patients, there is a high incidence of ultrasound work-related musculoskeletal disorders (WRMSD) among sonographers. According to a recent publication, patient obesity is reported as the most significant barrier to practicing ergonomic scanning techniques.4
Meet the DAX
An innovative solution to reduce transducer pressure
To help you address your bariatric patient population, Siemens Healthineers conducted extensive research to find a solution that allows clinicians to image patients varying in size with confidence and clarity. From this research, a new transducer has emerged – DAX.
The new DAX (Deep Abdominal Transducer) is a unique and patented imaging transducer that allows clinicians to image high BMI patients with confidence. Together with the ACUSON Sequoia ultrasound system, you can now deliver images at depths up to 40 cm without compromising diagnostic quality.
Advanced Multi-D beam formation enables DAX to penetrate up to 40 cm
High element density transducers allow dynamic elevation aperture control according to one’s imaging needs. By changing the shape of the acoustic transmit signal, clinicians are able to clearly focus on smaller regions of interest than ever before while maintaining elevation slice thickness throughout the image.
The DAX employs an advanced form of Multi-D beam formation for images at depths up to 40 cm, helping clinicians to better detect focal lesions in high-BMI patients and reduce diagnostic uncertainty and potentially unnecessary patient testing.
Case Studies


Case study courtesy of Richard G. Barr MD, PhD
Liver Elastography Comparison
47-year old male - BMI 33.3 (Obese)
Indication: NAFLD follow-up
Conventional Ultrasound Elastography Results:
ACUSON Sequoia Elastography Results:
Case study courtesy of Richard G. Barr MD, PhD
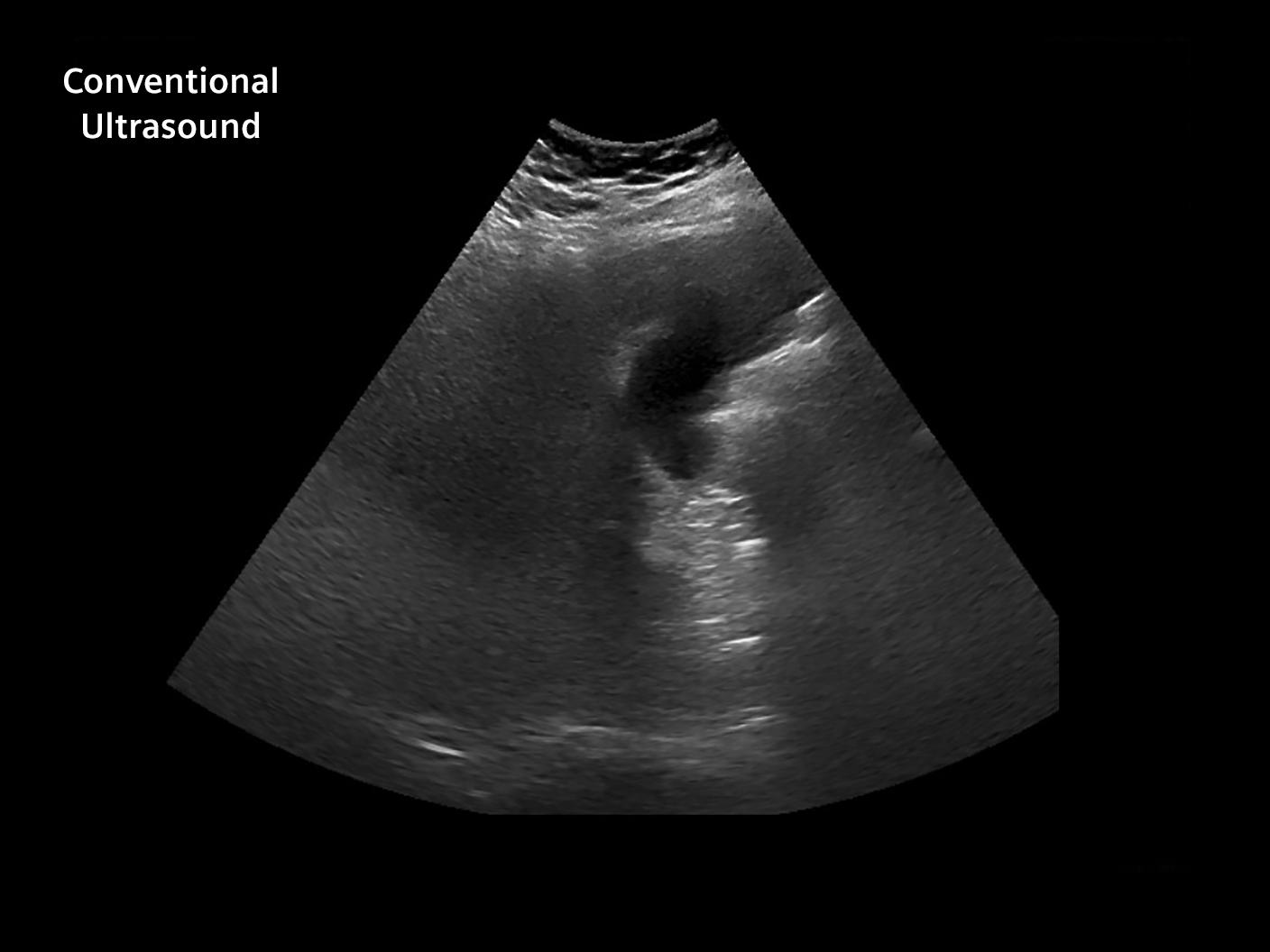
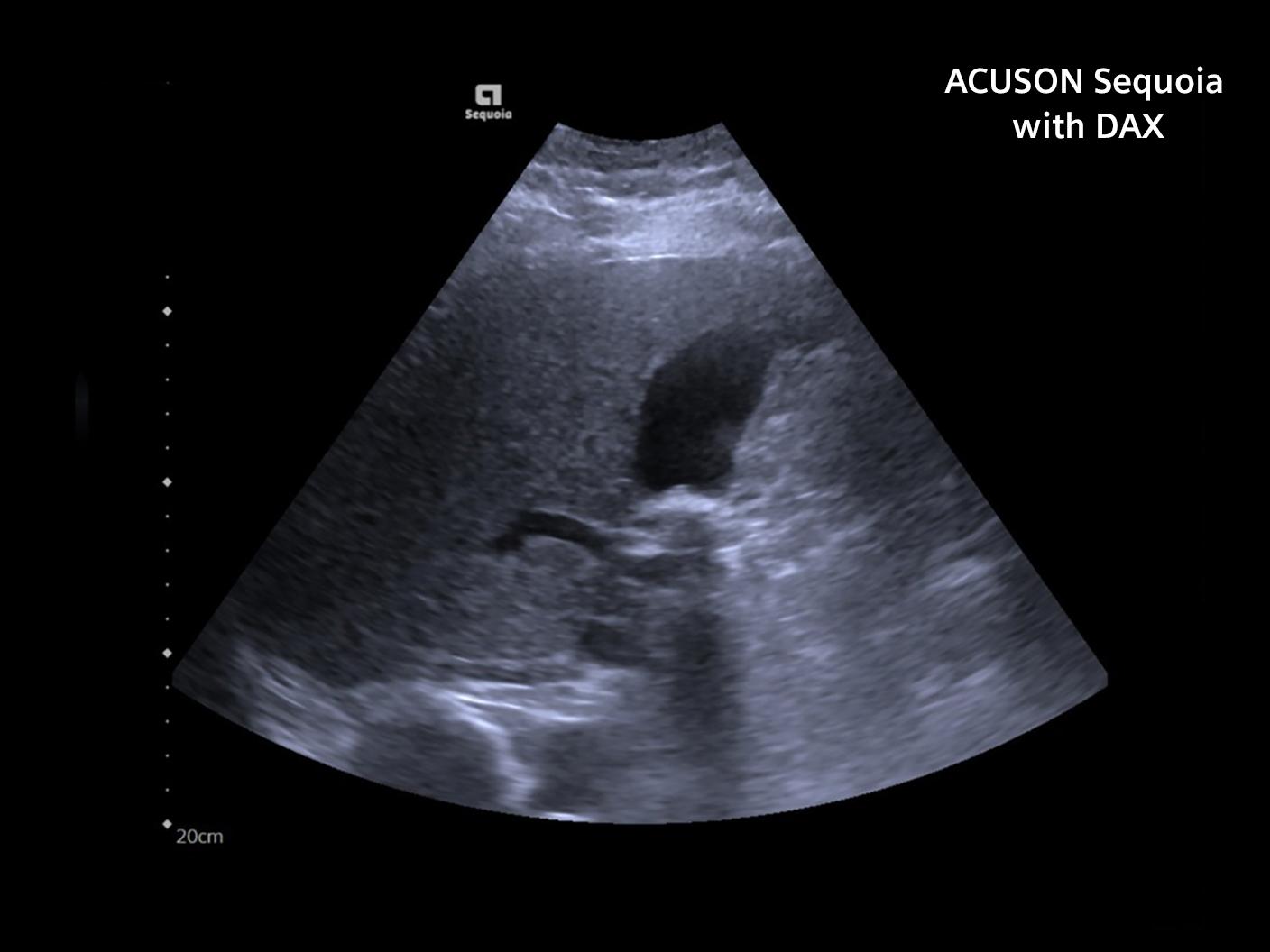
Liver/Gallbladder Comparison
69 year old male—BMI 41.6 (morbid obesity)
Indication: Abdominal Pain
Conventional Ultrasound Results:
- Limited due to body habitus
- Unable to obtain quality color in portal vein or hepatic veins
ACUSON Sequoia Results:
- Full qualitative liver evaluation
- Multiple mobile gallstones
- Good color Doppler Portal & Hepatic Veins


Case study courtesy of Richard G. Barr MD, PhD
Liver Elastography Comparison
47-year old male - BMI 33.3 (Obese)
Indication: NAFLD follow-up
Conventional Ultrasound Elastography Results:
ACUSON Sequoia Elastography Results:


Case study courtesy of Richard G. Barr MD, PhD
Liver/Gallbladder Comparison
69 year old male—BMI 41.6 (morbid obesity)
Indication: Abdominal Pain
Conventional Ultrasound Results:
- Limited due to body habitus
- Unable to obtain quality color in portal vein or hepatic veins
ACUSON Sequoia Results:
- Full qualitative liver evaluation
- Multiple mobile gallstones
- Good color Doppler Portal & Hepatic Veins


Case study courtesy of Richard G. Barr MD, PhD
Liver Elastography Comparison
47-year old male - BMI 33.3 (Obese)
Indication: NAFLD follow-up
Conventional Ultrasound Elastography Results:
ACUSON Sequoia Elastography Results:




Testimonials
Learn how Diana Neuhardt takes on the most difficult vascular challenges with the DAX transducer
Learn how Dr. Barr is using the DAX to improve disease detection
Learn how Diana Neuhardt takes on the most difficult vascular challenges with the DAX transducer
Learn how Dr. Barr is using the DAX to improve disease detection
Learn how Diana Neuhardt takes on the most difficult vascular challenges with the DAX transducer
More Information
Did this information help you?
Thank you.
The statements by Siemens’ Healthineers customers described herein are based on results that were achieved in the customer's unique setting. Because there is no "typical" hospital or laboratory and many variables exist (e.g., hospital size, samples mix, case mix, level of IT and/or automation adoption) there can be no guarantee that other customers will achieve the same results.
https://www.diagnosticimaging.com/view/challenges-imaging-obese-patients
https://www.webmd.com/diet/obesity/news/20170803/fat-shaming-patients-can-cause-real-harm
https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/article-abstract/2656710
Scholl, C., and Salisbury, H. (2017). Barriers to Performing Ergonomic Scanning Techniques for Sonographers. J. Diagnostic Med. Sonogr. 33, 406–411.
