Reveal fine details in the brain
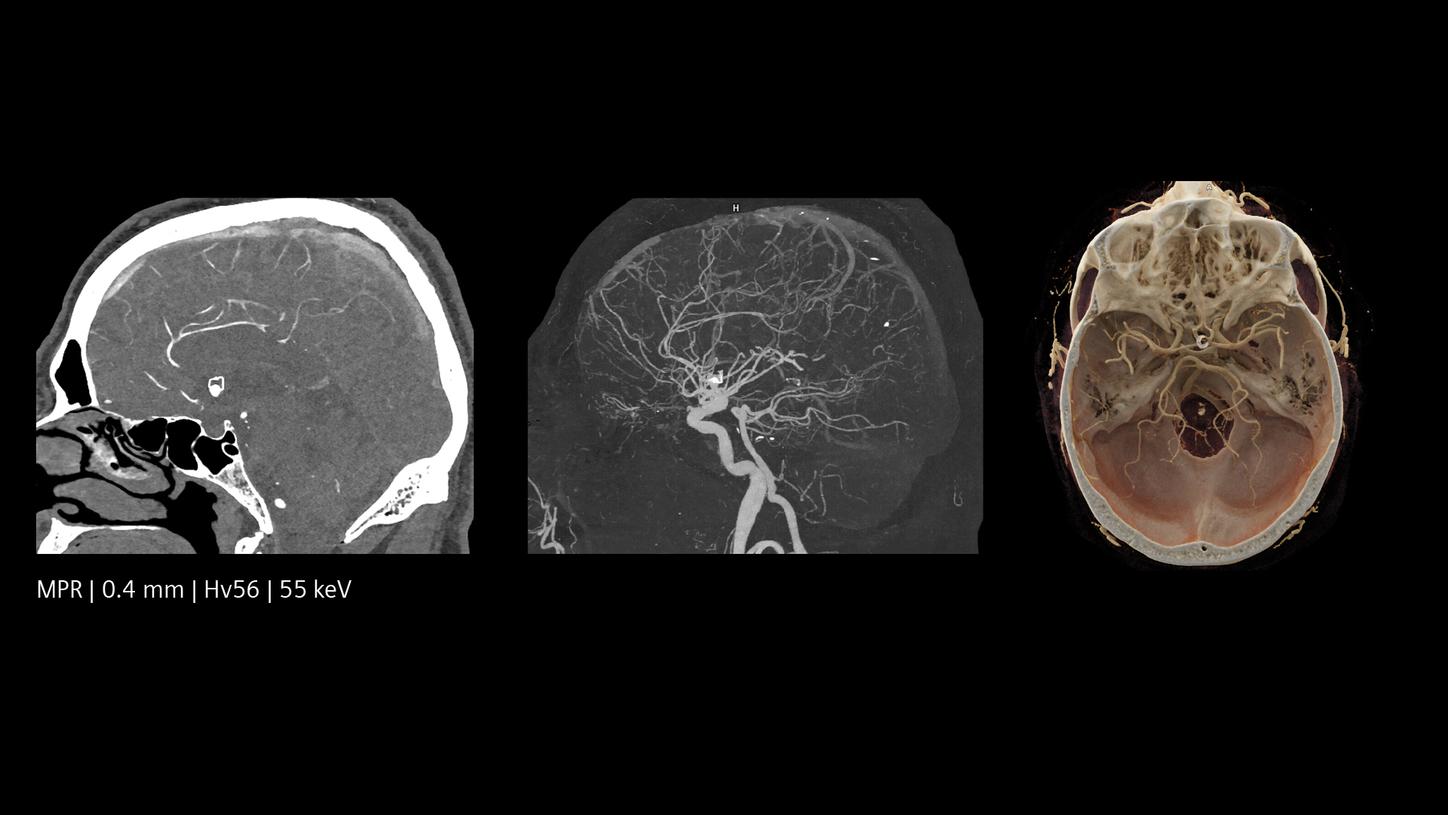
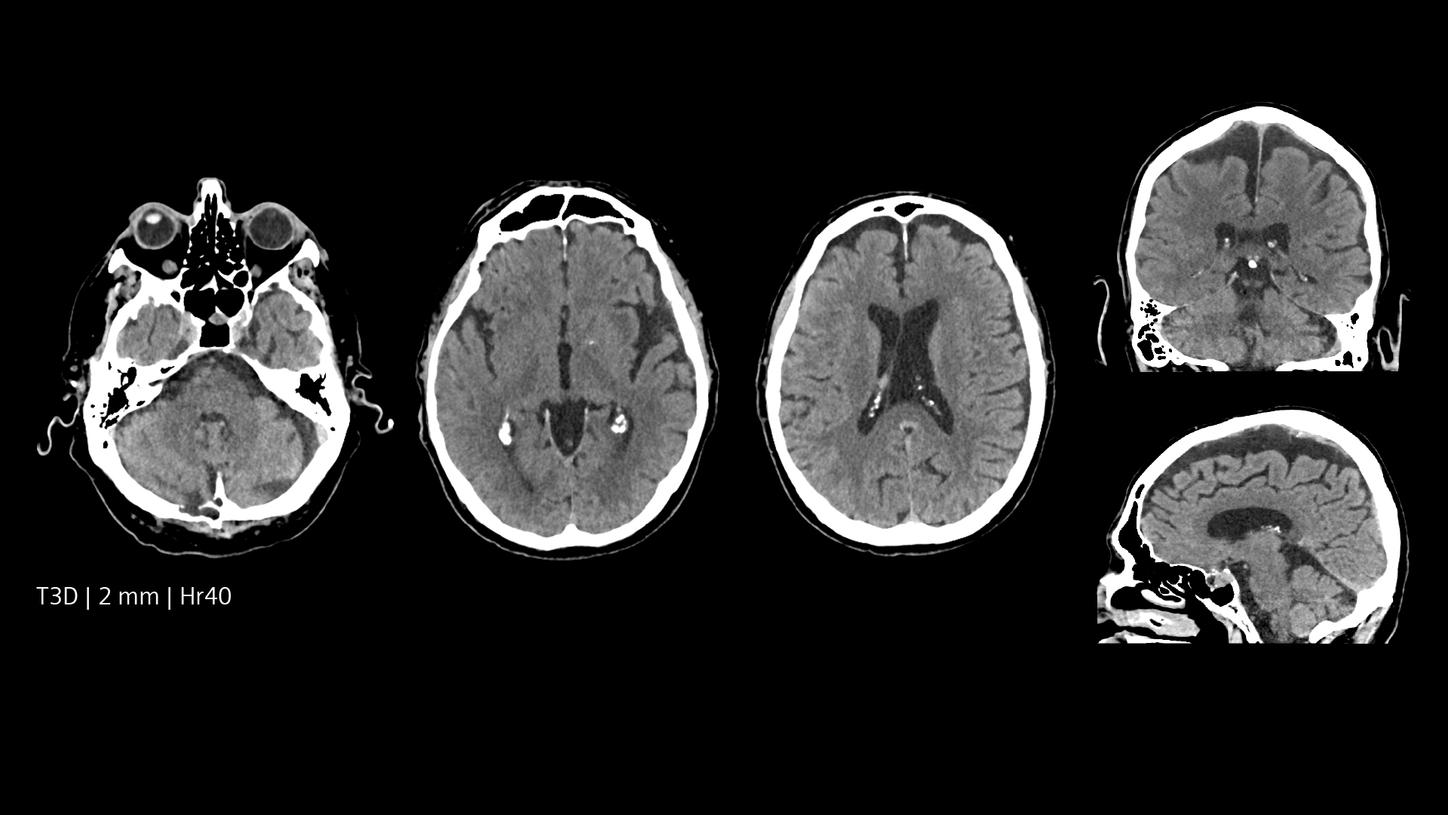
The NAEOTOM® Alpha class with Quantum Technology represents a quantum leap for high resolution CT imaging. Changing the dose vs. image-quality equation substantially, it offers a whole new level of detail while keeping dose to a minimum. Visualize small lesions and fine details – to aid clinical decisions in neurology.
Increased resolution, both in-plane and cross-plane, inherently available spectral imaging options, better image quality, and improved dose efficiency combine to enable a change at the front line of stroke and neurological care. Physicians can gain insight into details of the brain previously inaccessible or only accessible with greater effort. Say goodbye to compromising between resolution and dose, and provide more answers to more patients.
Redefining imaging at the front line of stroke care
At the Erasmus Medical Center in Rotterdam, the Netherlands, NAEOTOM Alpha with Quantum Technology has eclipsed conventional high-end CT scanners. Radiologist Anke van der Eerden, MD, talks about how Quantum HD ultra-thin slice thickness (up to just 0.2 mm) at standard dose has made all the difference and paved the way for photon-counting CT in clinical routine.
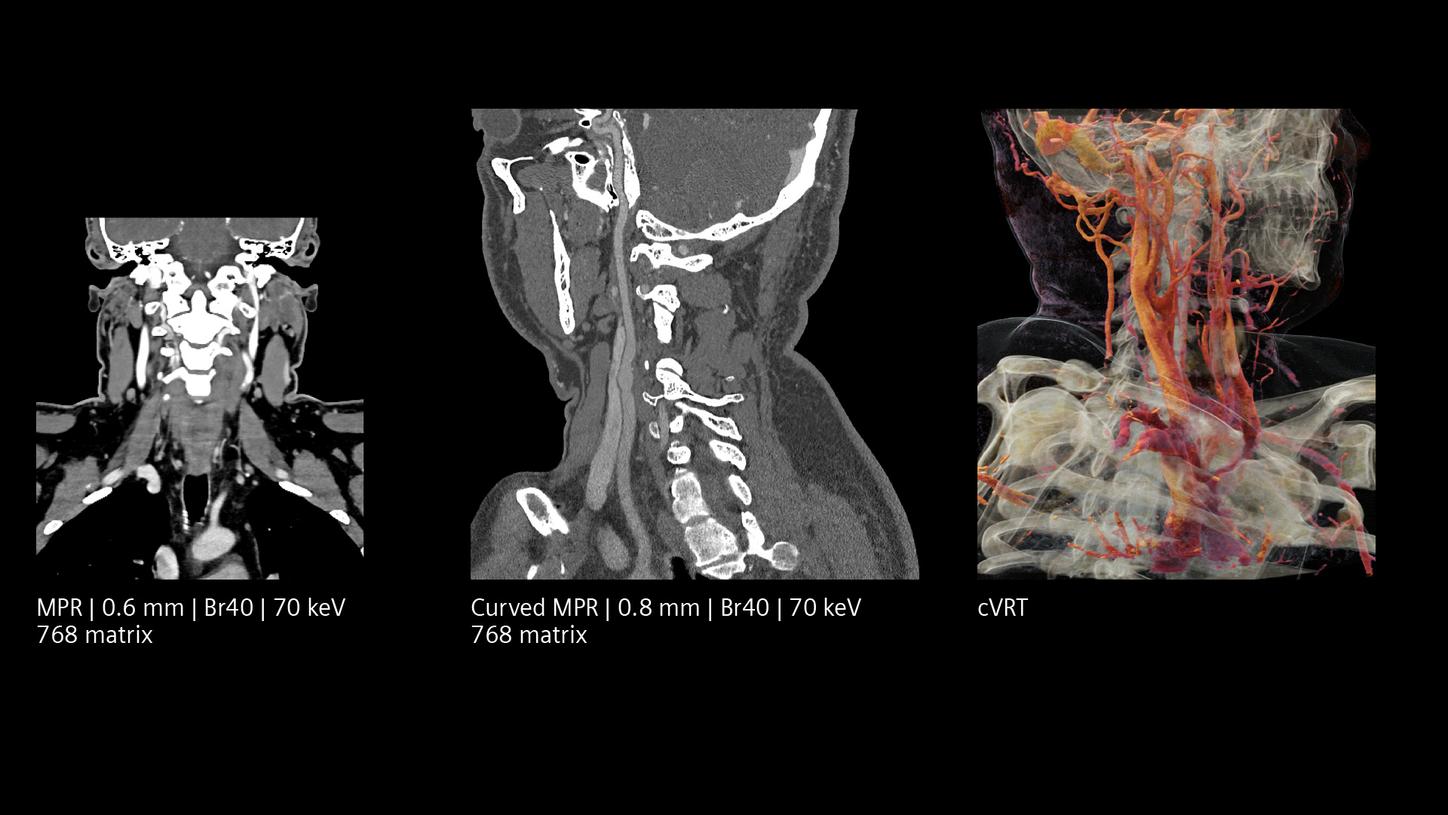
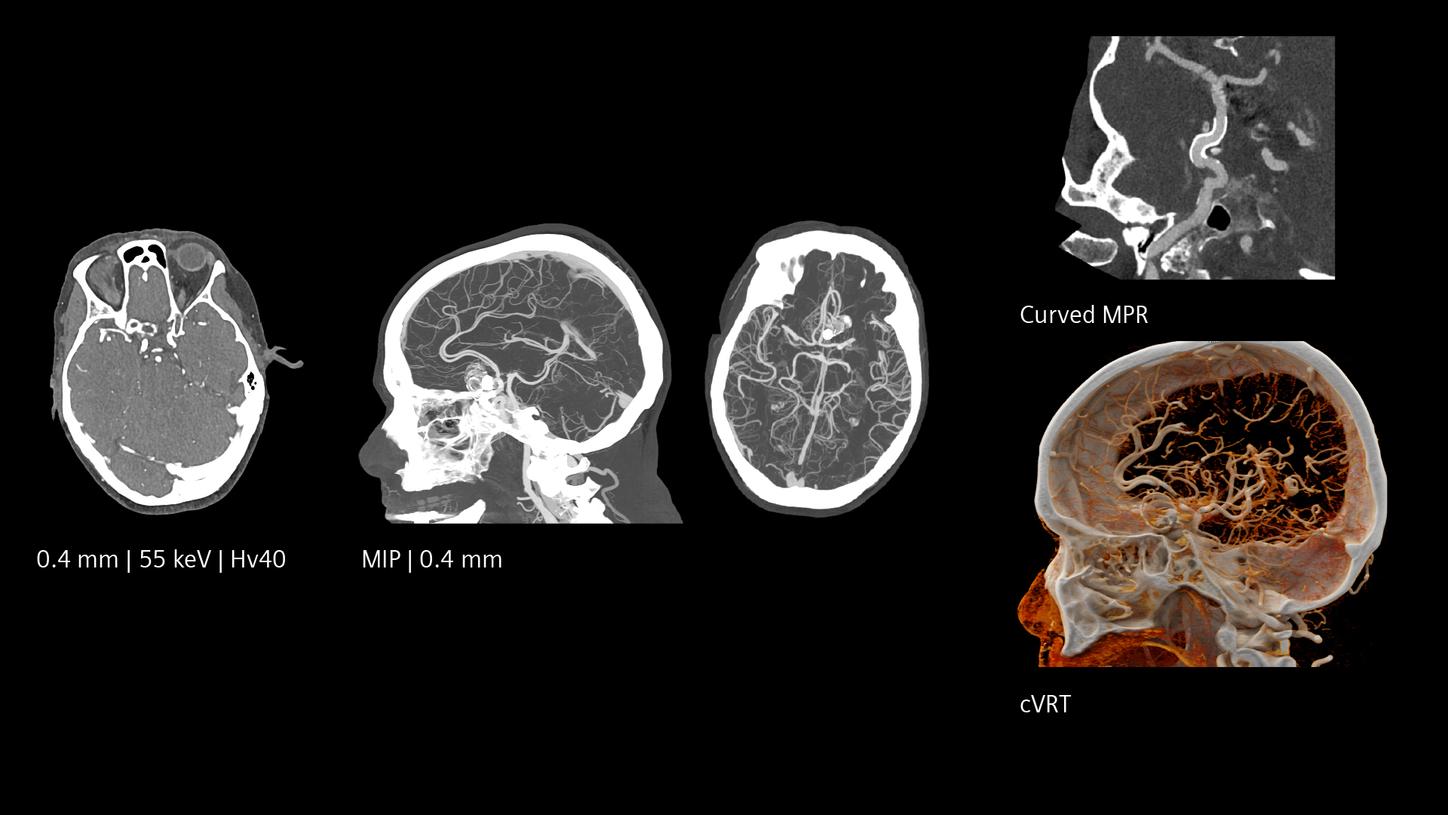
Ultra-high resolution both in-plane and cross-plane
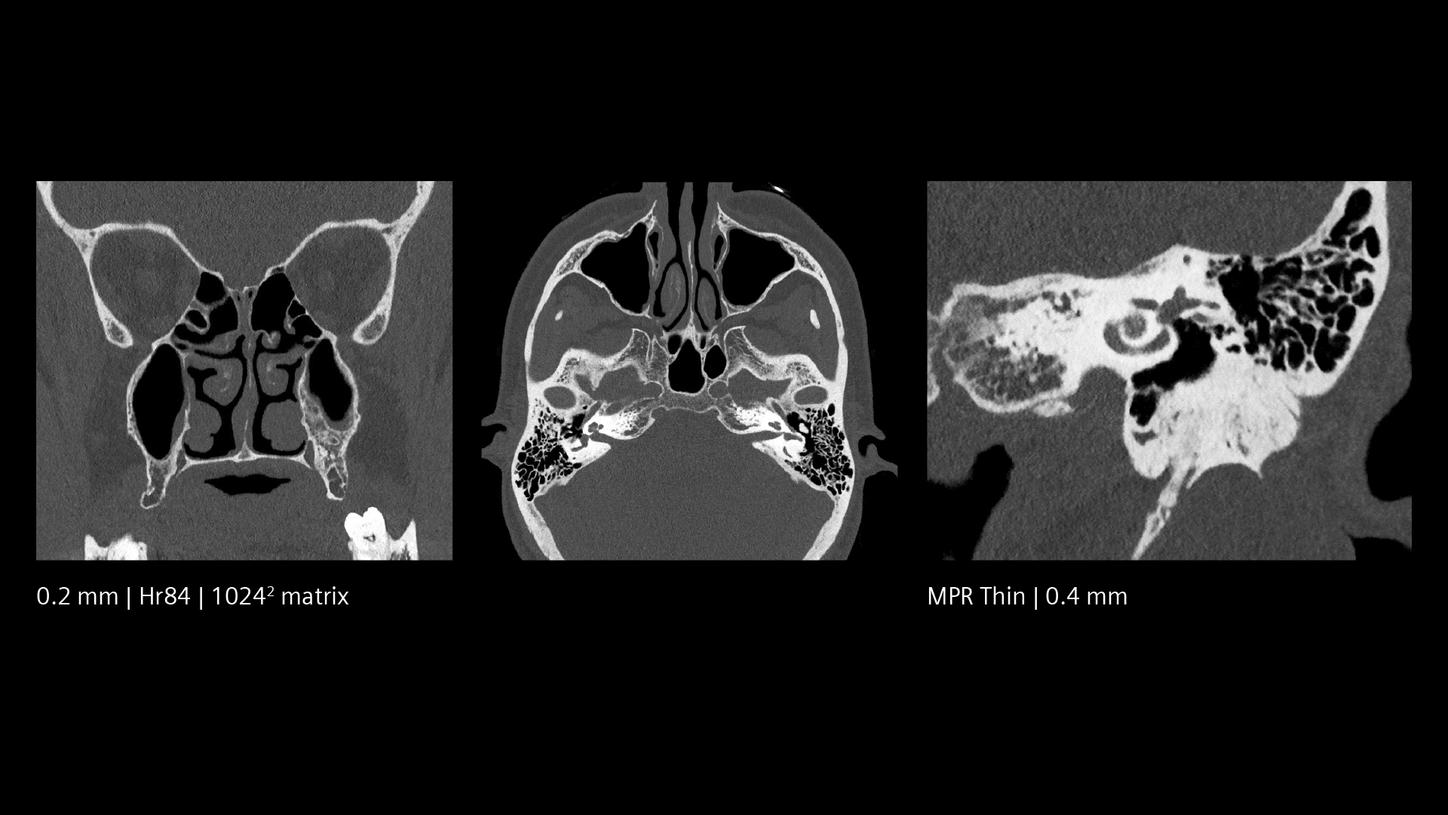
Quantum HD images created by NAEOTOM Alpha offer optimized results without a dose increase. They make it possible to differentiate between white and grey matter with precision at low keV levels. Quantum Spectral Imaging is inherently available without additional scans or effort. See for yourself.

The Netherlands
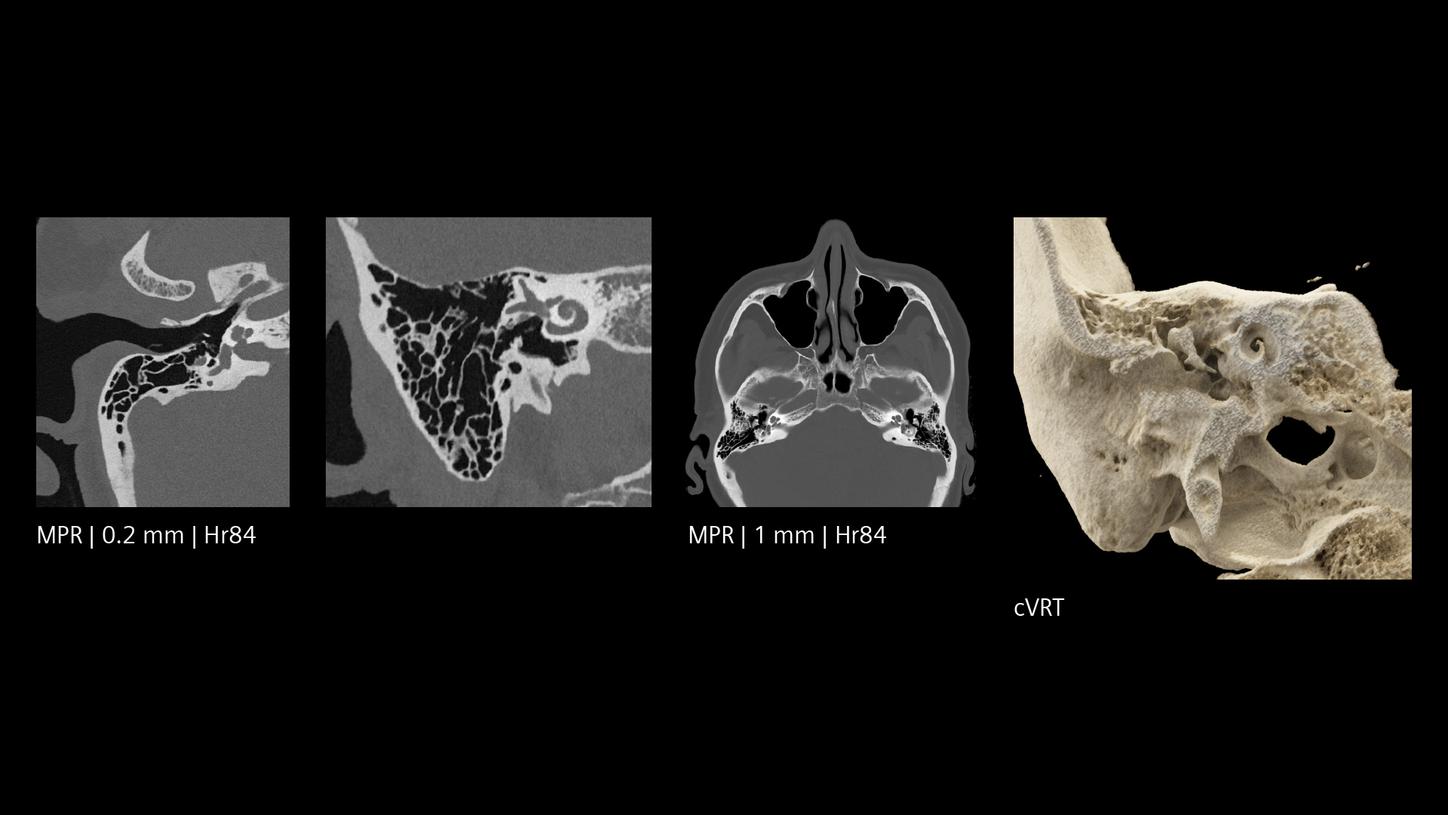
Ultra-high resolution in clinical routine
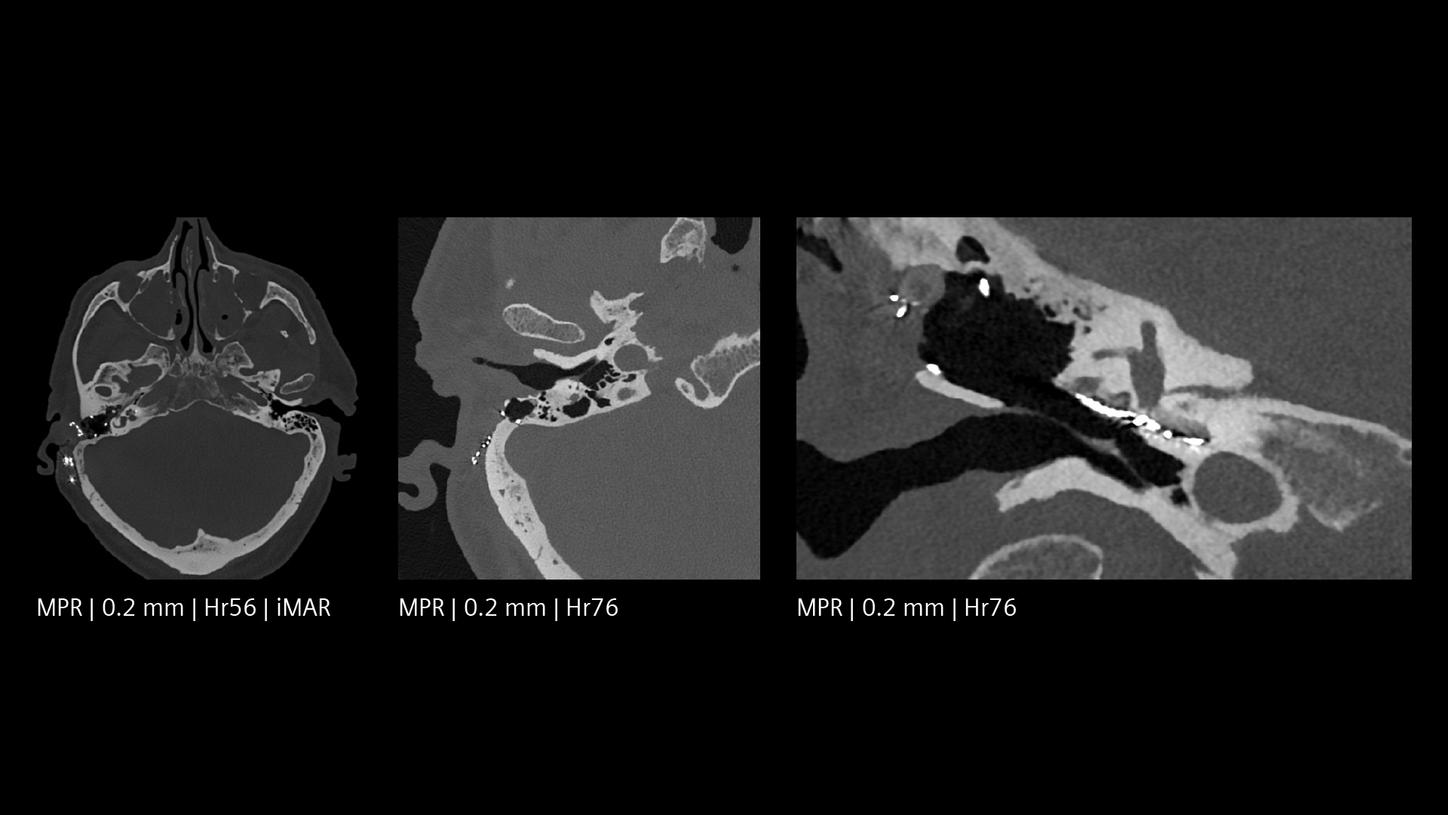
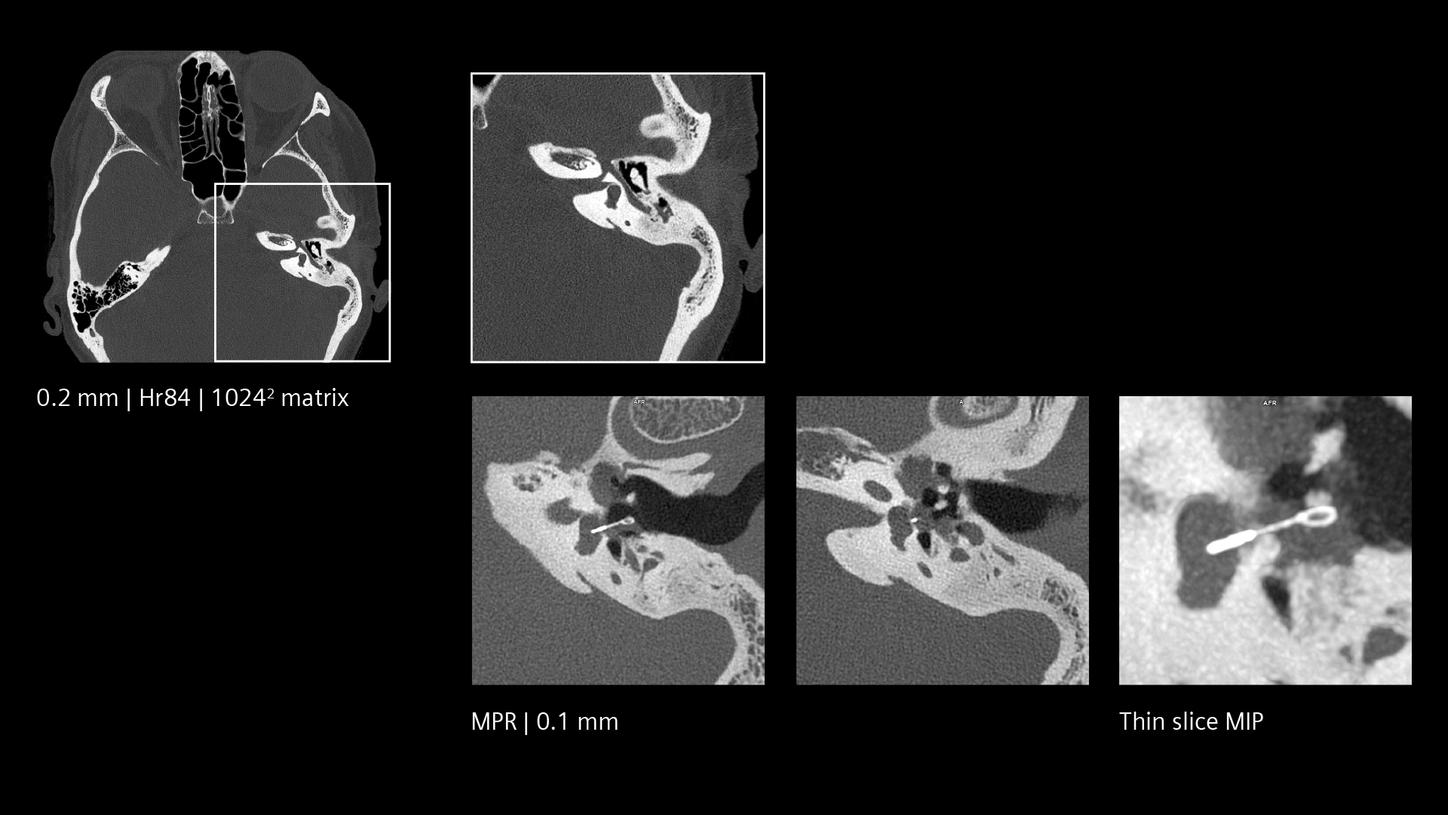
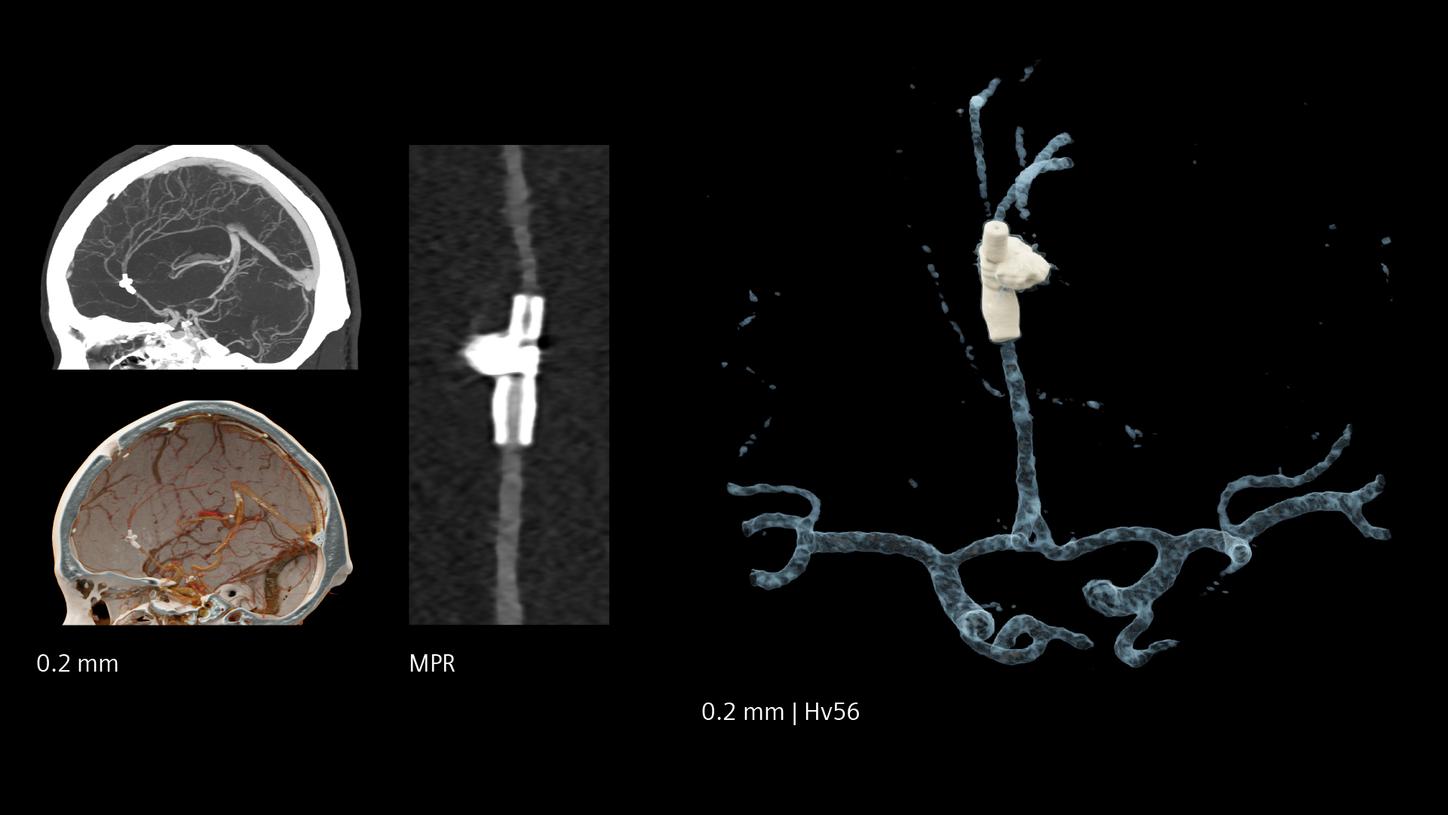
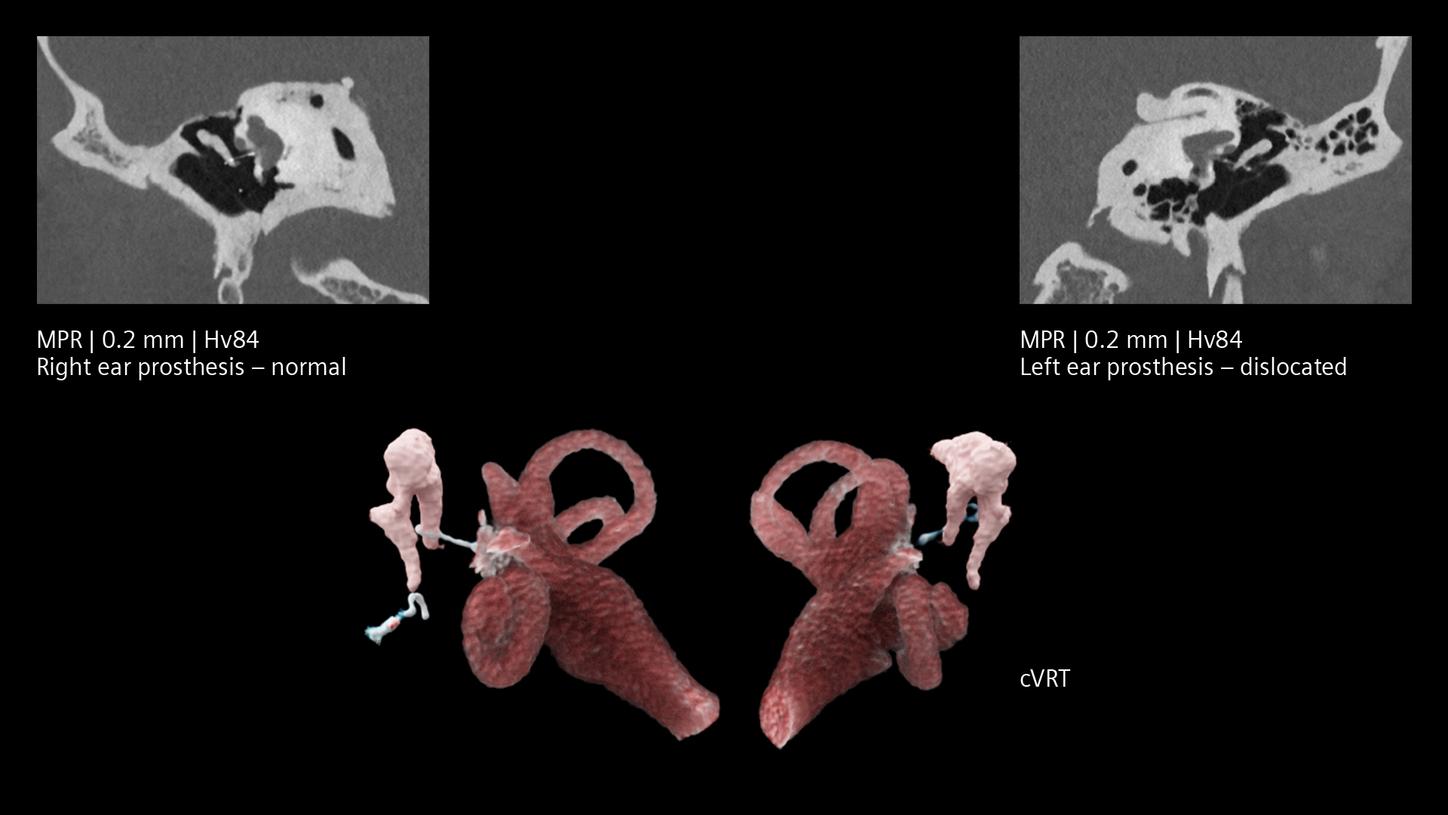
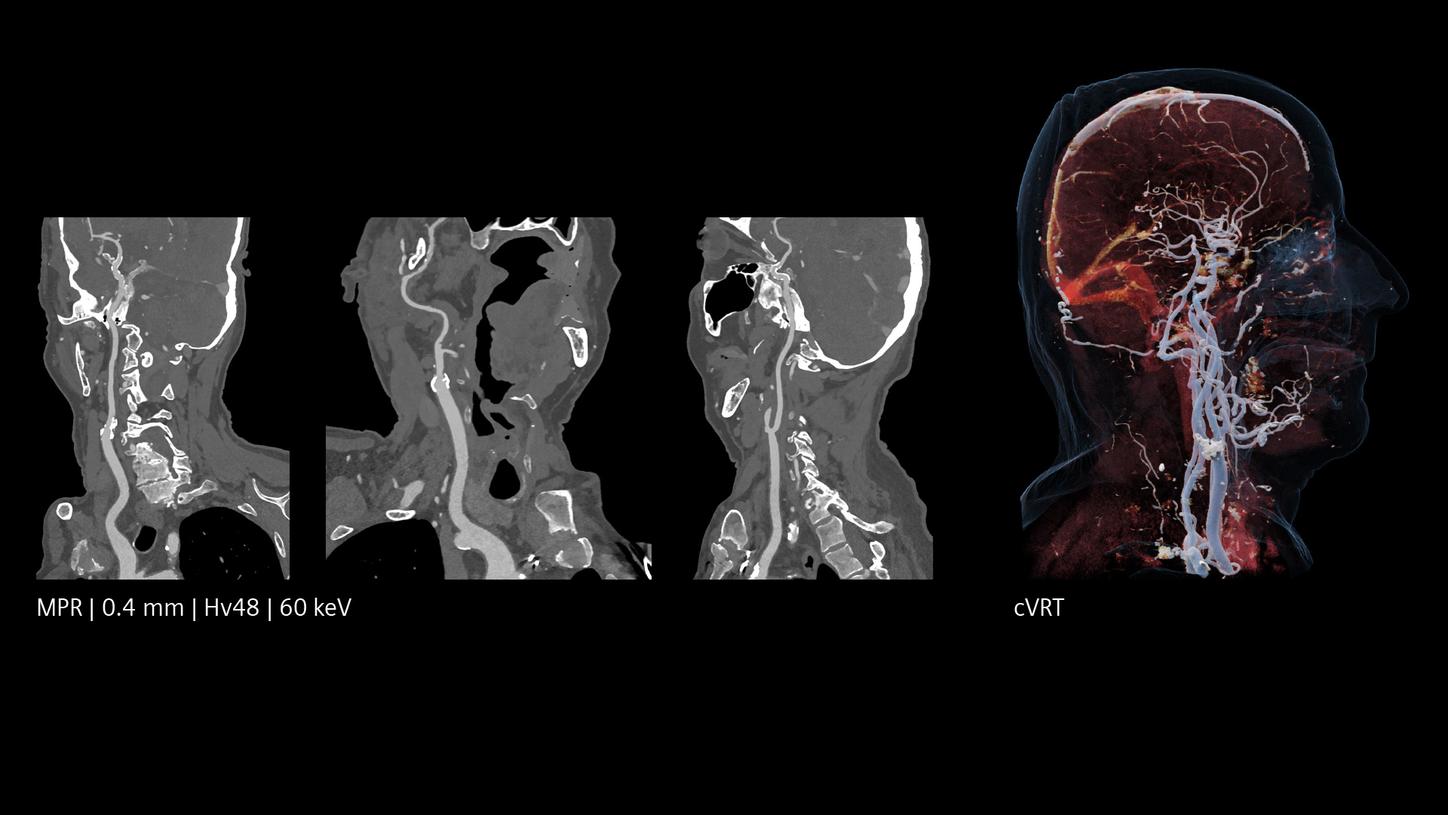
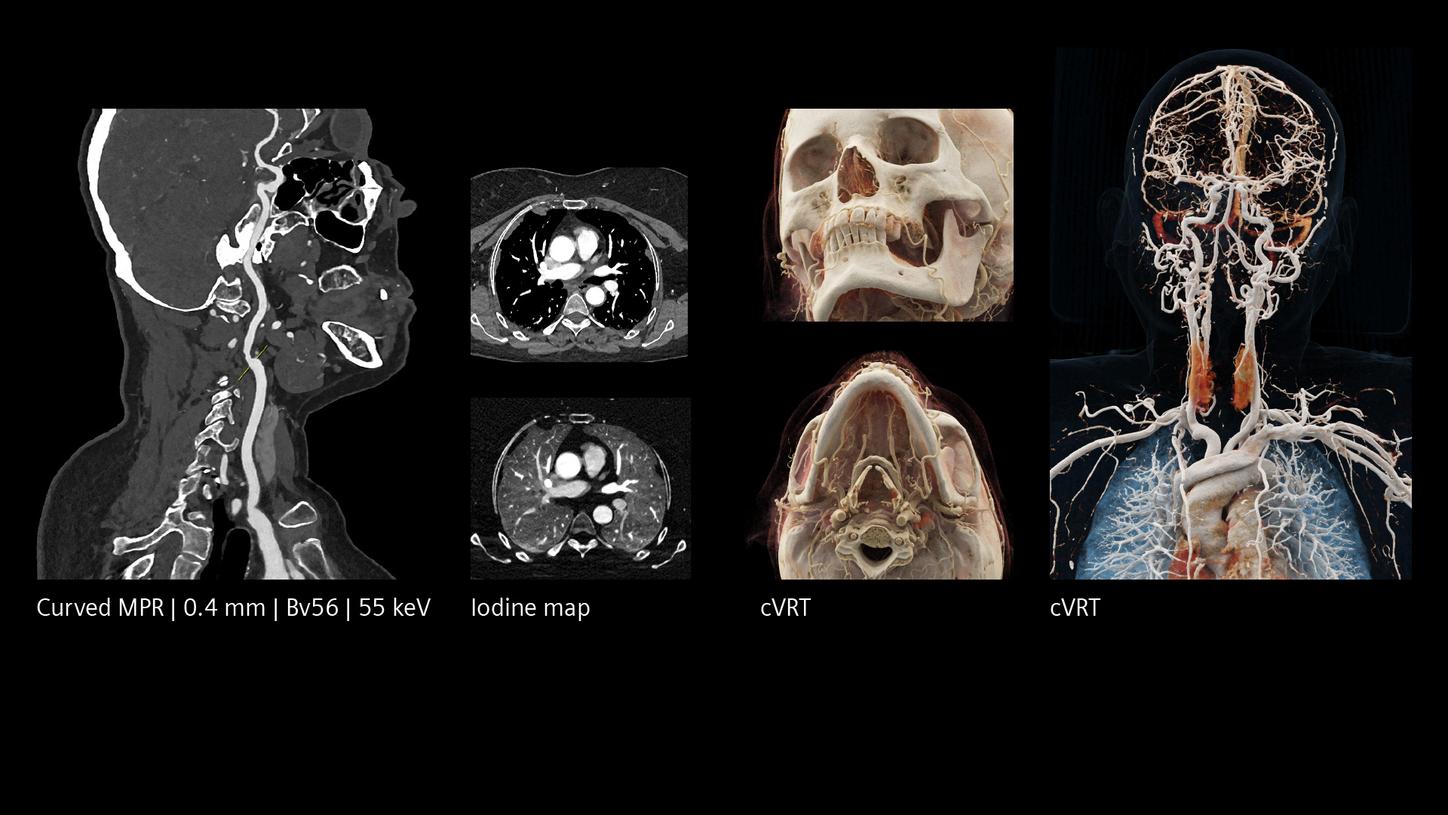
The NAEOTOM Alpha class and its Quantum HD images come with a slice thickness of just 0.2 mm as available with all NAEOTOM Alpha class systems. The technology reduces radiation-dose concerns about ultra-high resolution scanning and holds the potential to extend the utilization of ultra-high resolution imaging to a broader range of patients. Head scans are routinely prone to metal artifacts caused by dental implants, coils, flow diverters, and stents. Inherently available Quantum Spectral Imaging helps reduce these metal artifacts for neurovascular applications, which can add clarity to diagnostic assessments.

The Netherlands
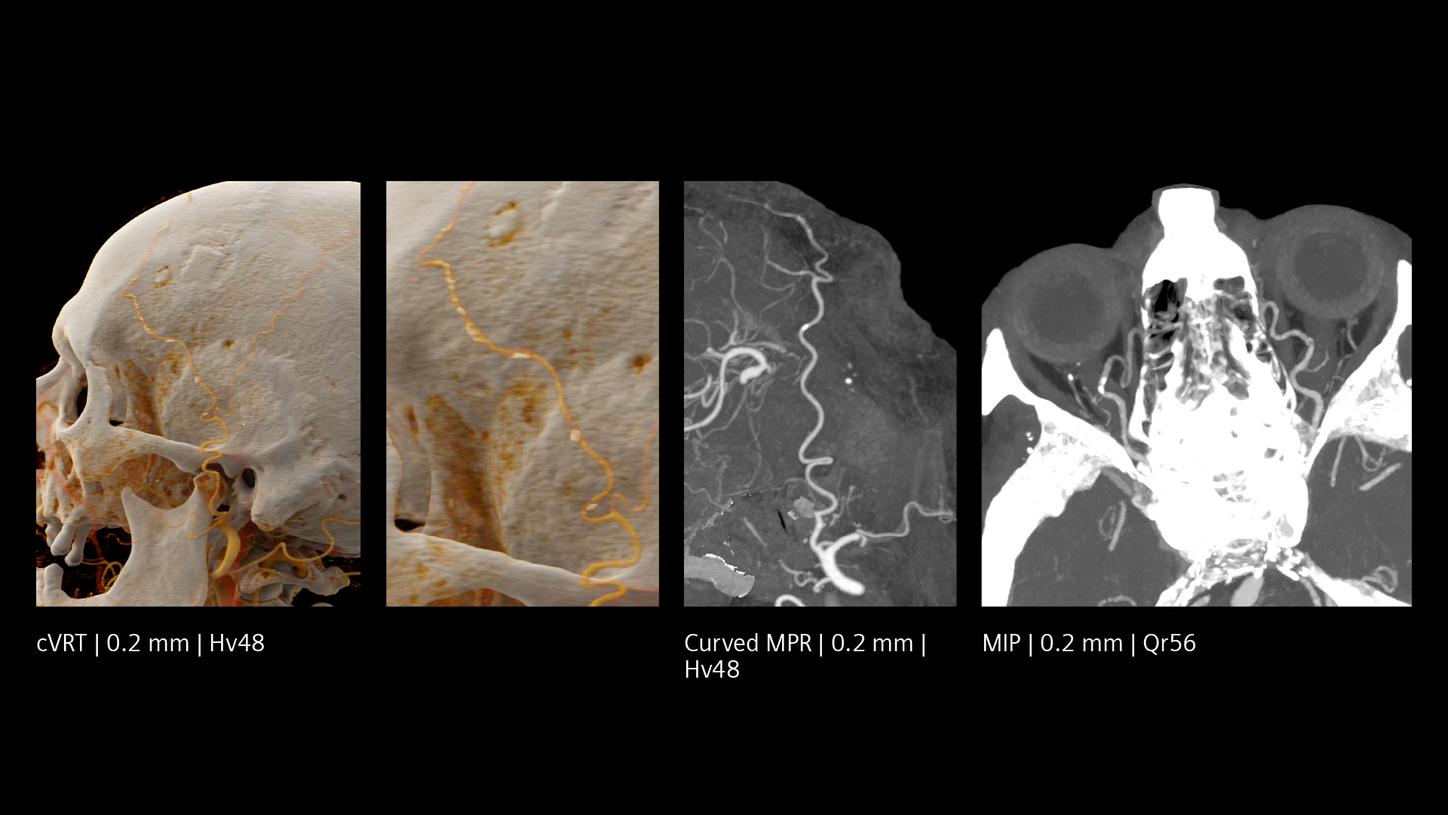
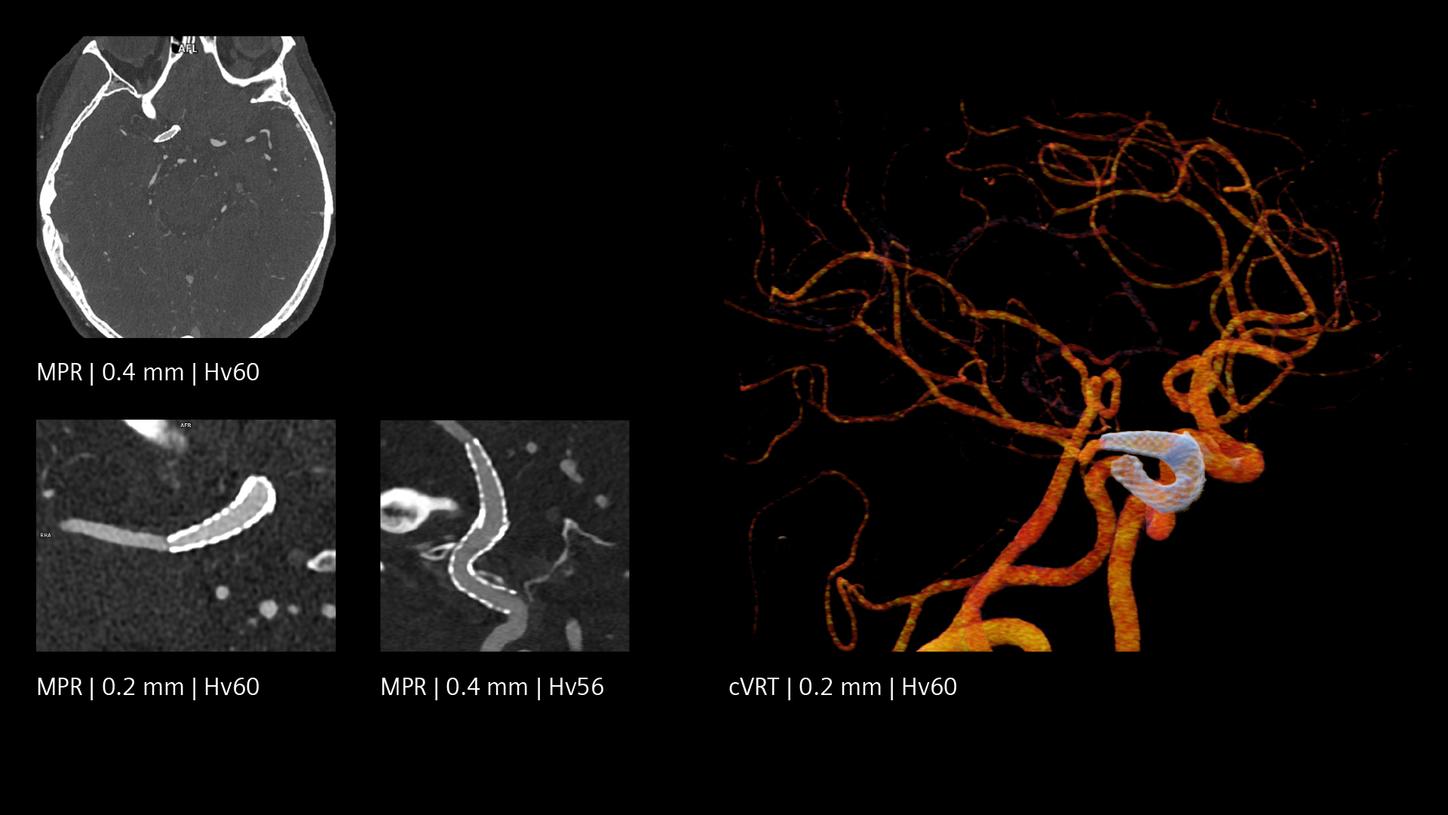
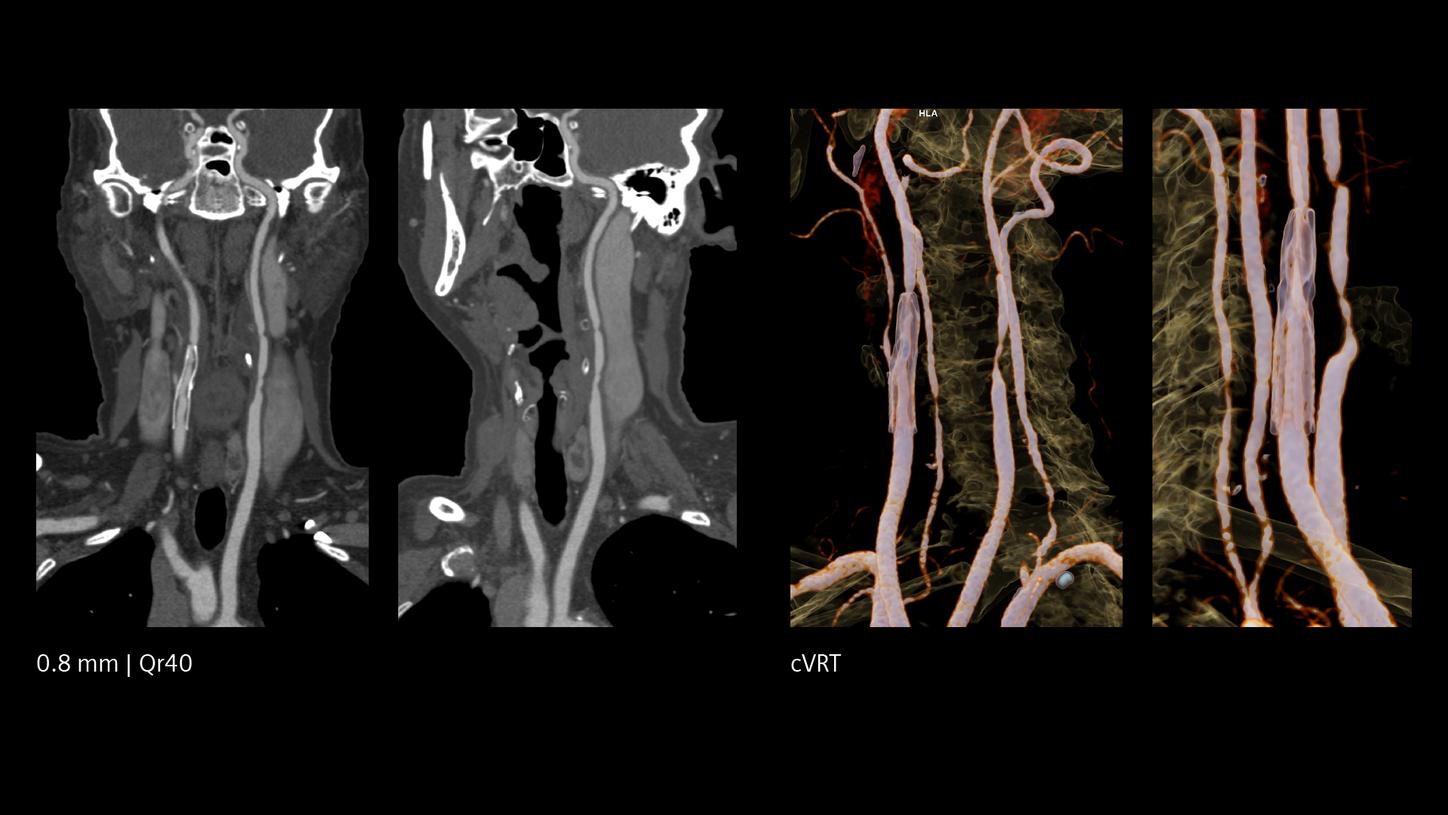
Increased visibility of smaller vessels
The unique Quantum Technology has the potential to reduce image noise and improve spatial and contrast resolution, pushing the boundaries for stroke pathways. This enables better visualization of small neurovascular structures and accurate characterization of vascular pathologies such as smaller vessel occlusions in ischemic stroke, aneurysm, arteriovenous malformations (AVMs), and stenoses.

New diagnostic tools for treatment decisions
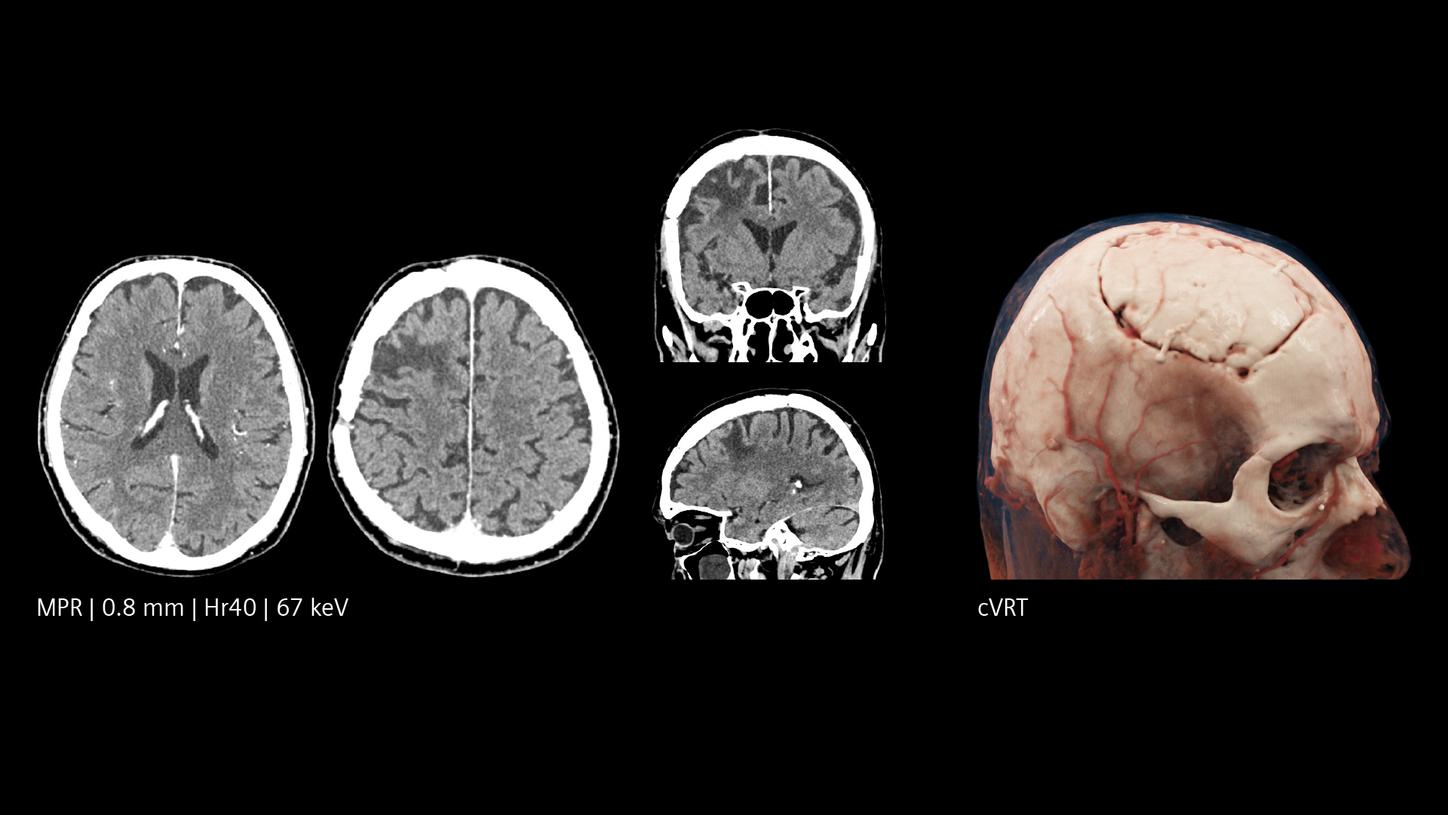
Revealing fine details at a new level of resolution, Quantum Technology in the NAEOTOM Alpha class can contribute to diagnostic certainty. This applies especially in challenging scenarios, such as patients with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) venous fistula, where the diagnosis changes patient’s well-being and quality of life.1
With NAEOTOM Alpha, we can optimize the visibility of medium- and small-sized arteries in the brain.2
Scientifically proven technology
Discover the full potential of the NAEOTOM Alpha class.
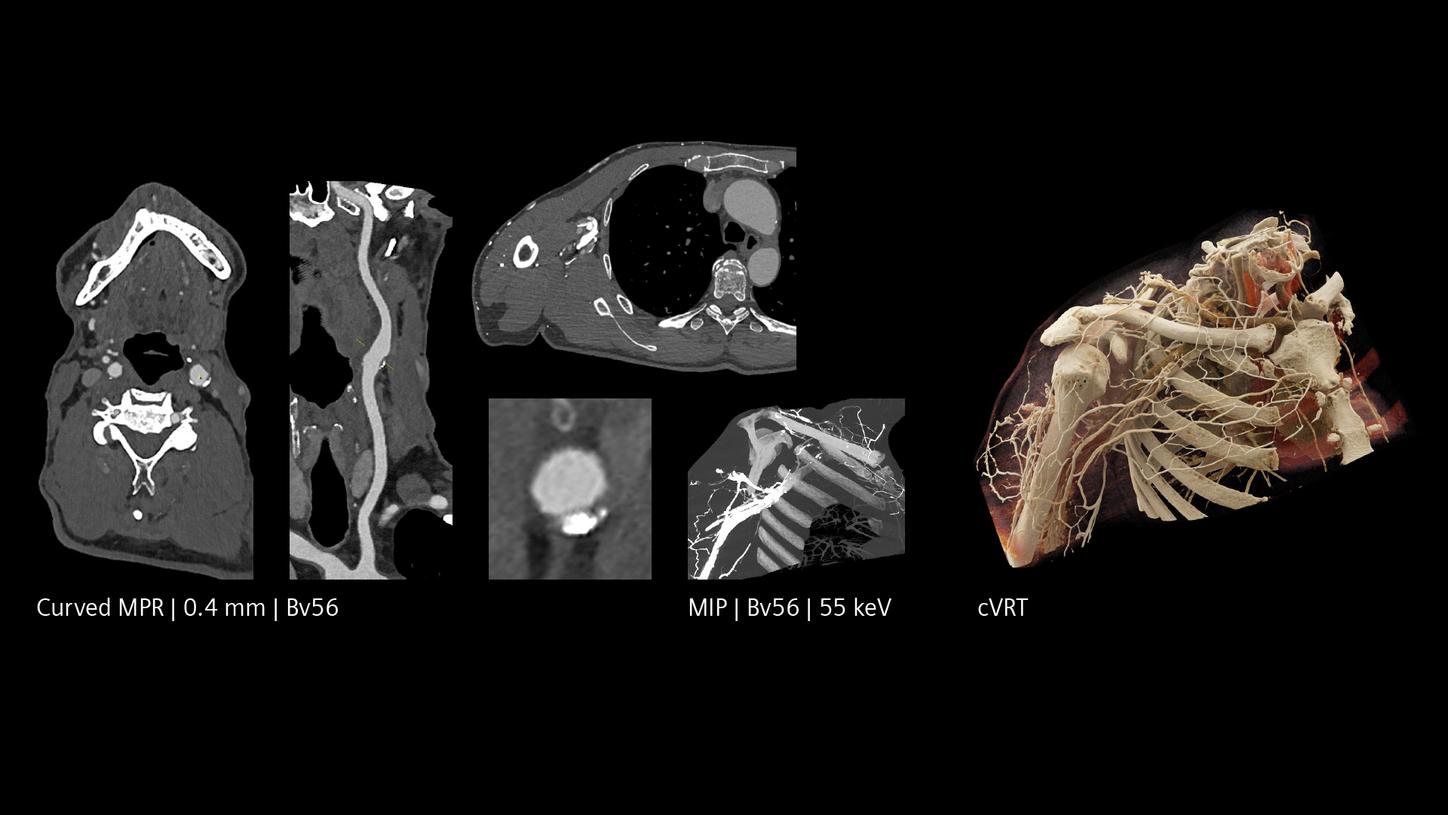
The NAEOTOM Alpha class in other clinical fields