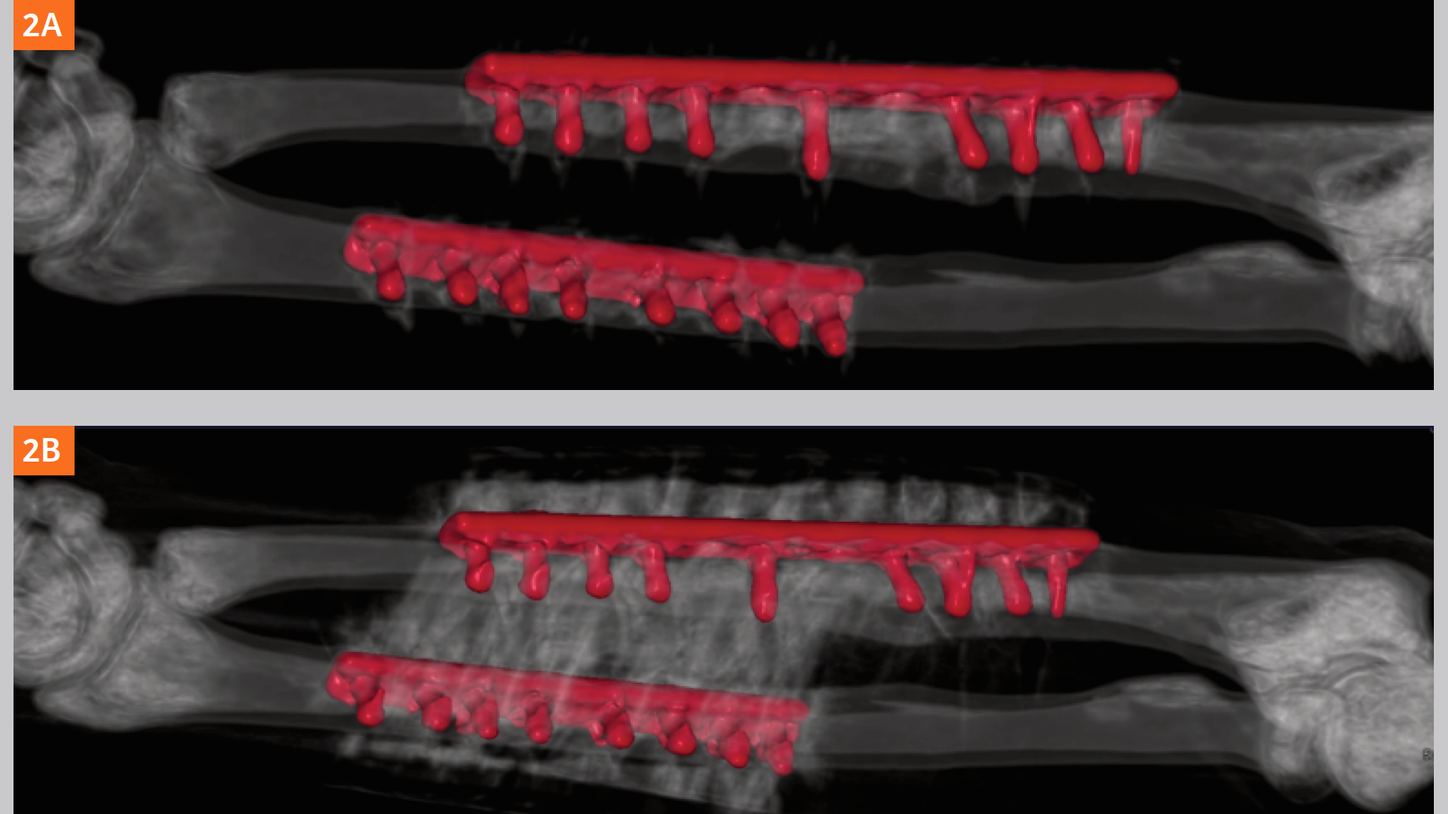
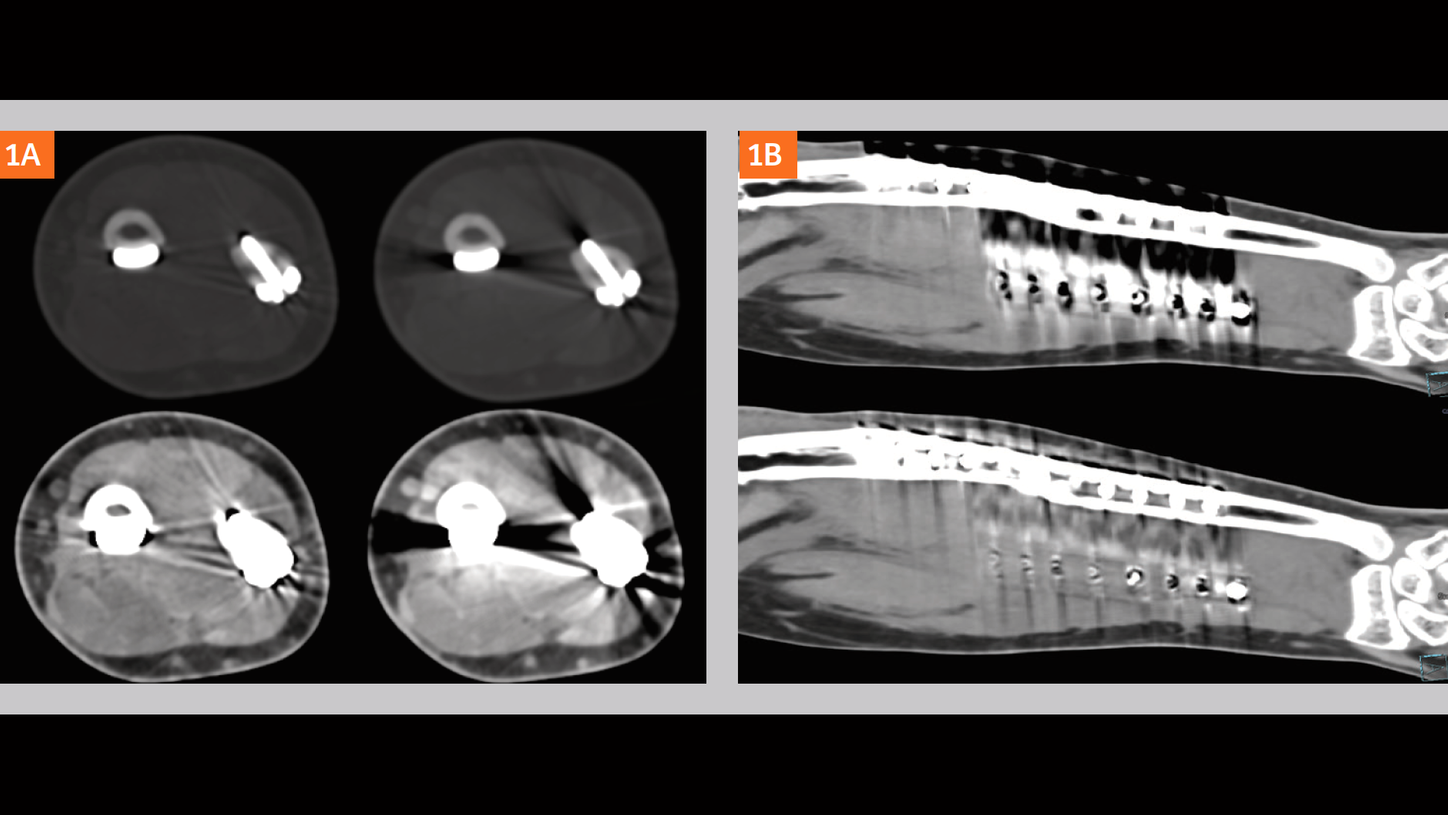
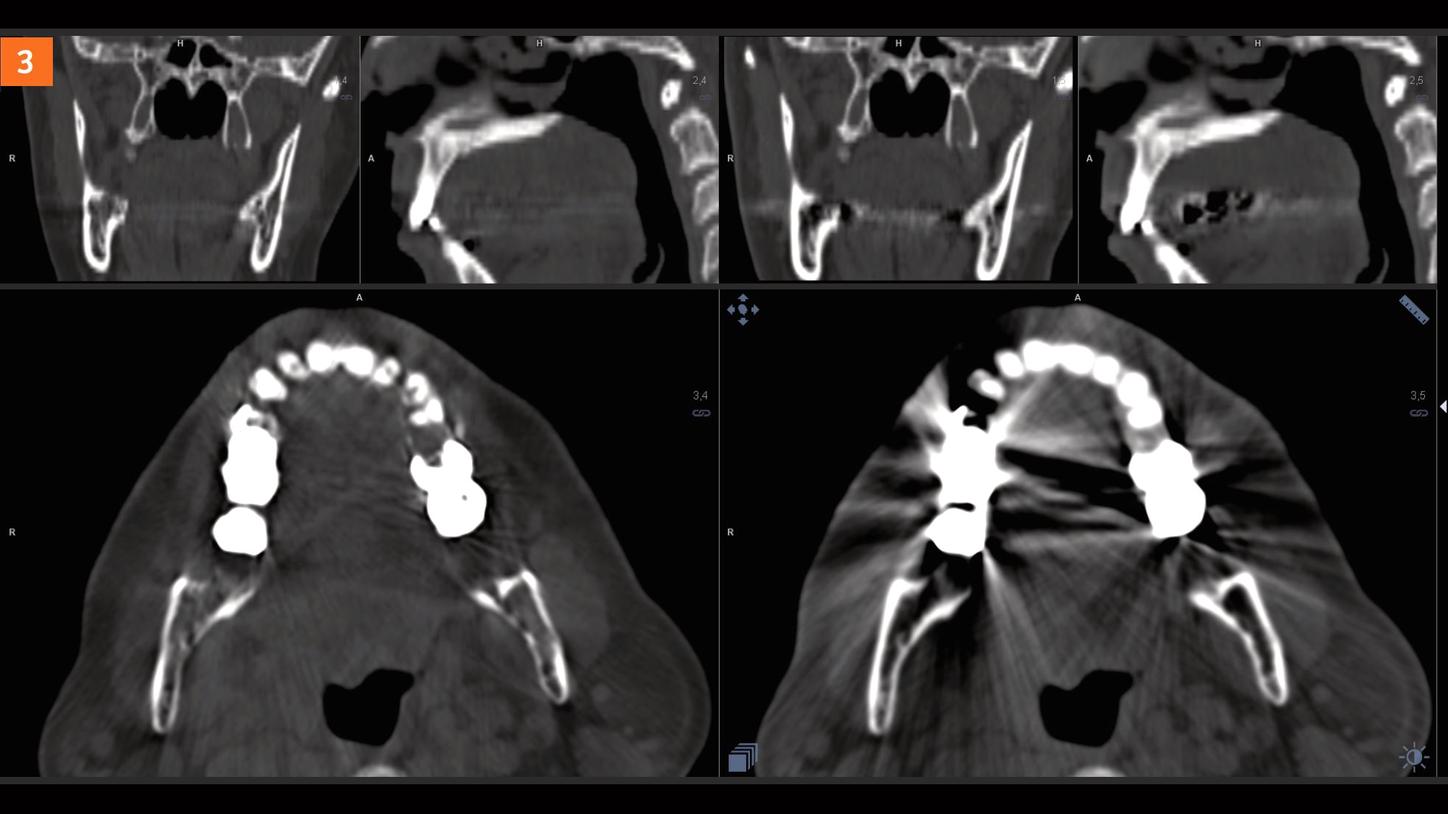
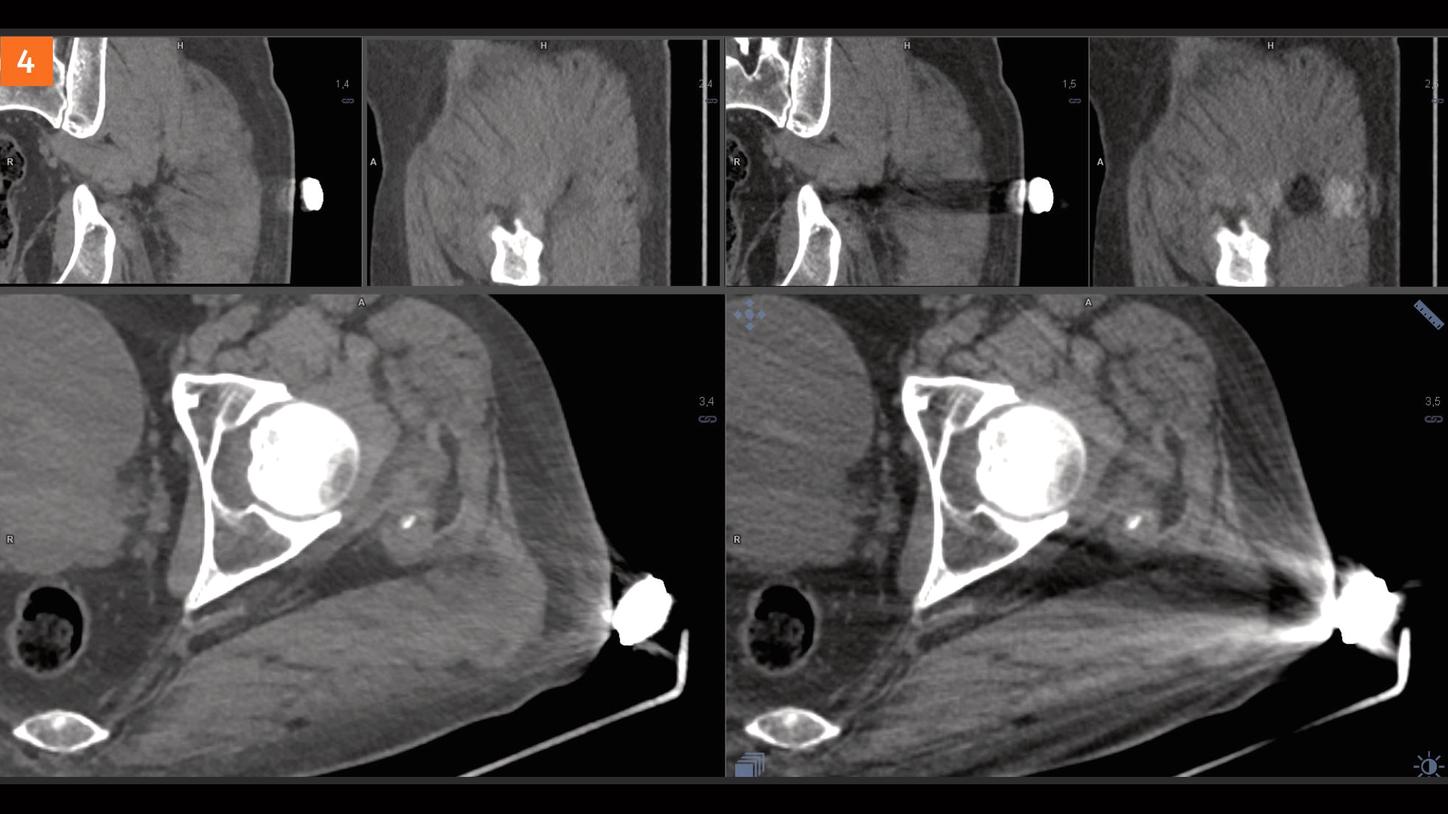
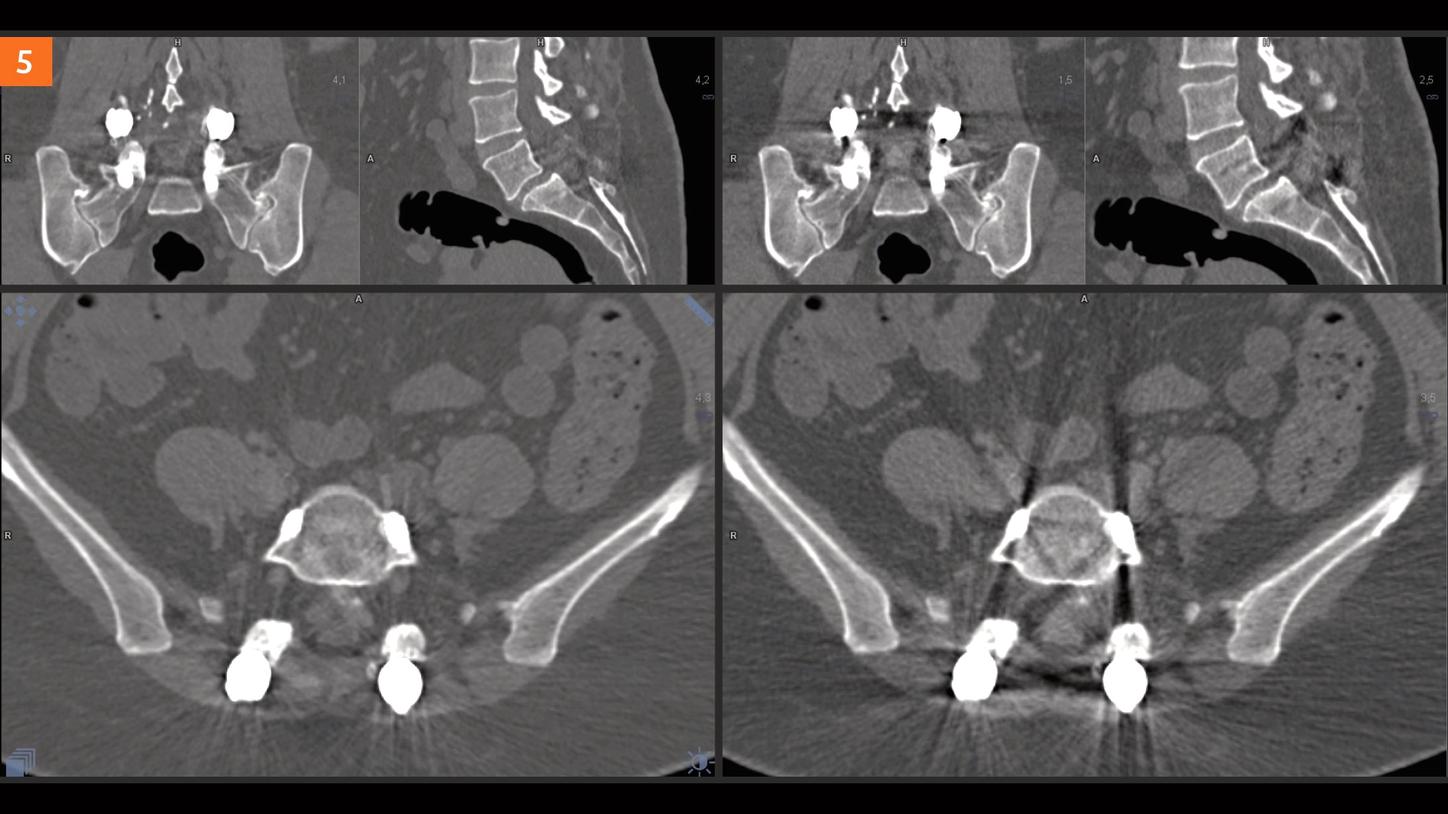
Conclusion
Clinical Support:
Khaled Elshamy, CT Application Specialist
Siemens Healthineers, Egypt
References
1. E. Bar, A. Schwahofer, S. Kuchenbecker, and P. Haring. Improving radiotherapy planning in patients with metallic implants using iterative metal artifact reduction (iMAR) algorithm. Biomed. Phys. Eng. Express 1 (2015): 1-12 https://www.rsna.org/education/rg_cme.html, https://pubs.rsna.org/doi/full/10.1148/radiol.13122089
2. Kurtz S, Ong K, Lau E, Mowat F, Halpern M. Projections of primary and revision hip and knee arthroplasty in the United States from 2005 to 2030. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2007; 89(4):780–785.
3. Meinel FG, Bischoff B, Zhang Q, Bamberg F, Reiser MF, Johnson TR. Metal artifact reduction by dual-energy computed tomography using energetic extrapolation: a systematically optimized protocol. Invest Radiol 2012; 47(7):406–414.
4. Meyer E, Raupach R, Lell M, Schmidt B, Kachelrieß M. Frequency split metal artifact reduction (FSMAR) in computed tomography. Med Phys 2012;39(4):1904–1916.
5. Feigenberg S. J., Paskalev K., McNeeley S., Horwitz E. M., Konski A., Wang L., Ma C., and Pollack A., “Comparing computed tomography localization with daily ultrasound during image-guided radiation therapy for the treatment of prostate cancer: A prospective evaluation,” J. Appl. Clin. Med. Phys. 8, 2268–2268 (2007).10.1120/jacmp.v8i3.2268 [PubMed] [CrossRef]
6. Wang J., Li T., and Xing L., “Iterative image reconstruction for CBCT using edge-preserving prior,” Med. Phys. 36, 252–260 (2009).10.1118/1.3036112 [PMC free article] [PubMed] [CrossRef]