RESOLVE
RESOLVE is a unique approach for obtaining high-quality, high-resolution DWI images even in body regions strongly affected by susceptibility artifacts. It is largely free of distortions and delivers sharp imaging at very higher spatial resolution. RESOLVE is especially attractive for the evaluation of smaller lesions in a wide range of DWI and DTI examinations. The practical value of this clinically decisive sequence can be further enhanced by Simultaneous Multi-Slice (SMS) acceleration. SMS can be combined with conventional parallel imaging and allows acquisition time gains as a factor of the slice acceleration.1


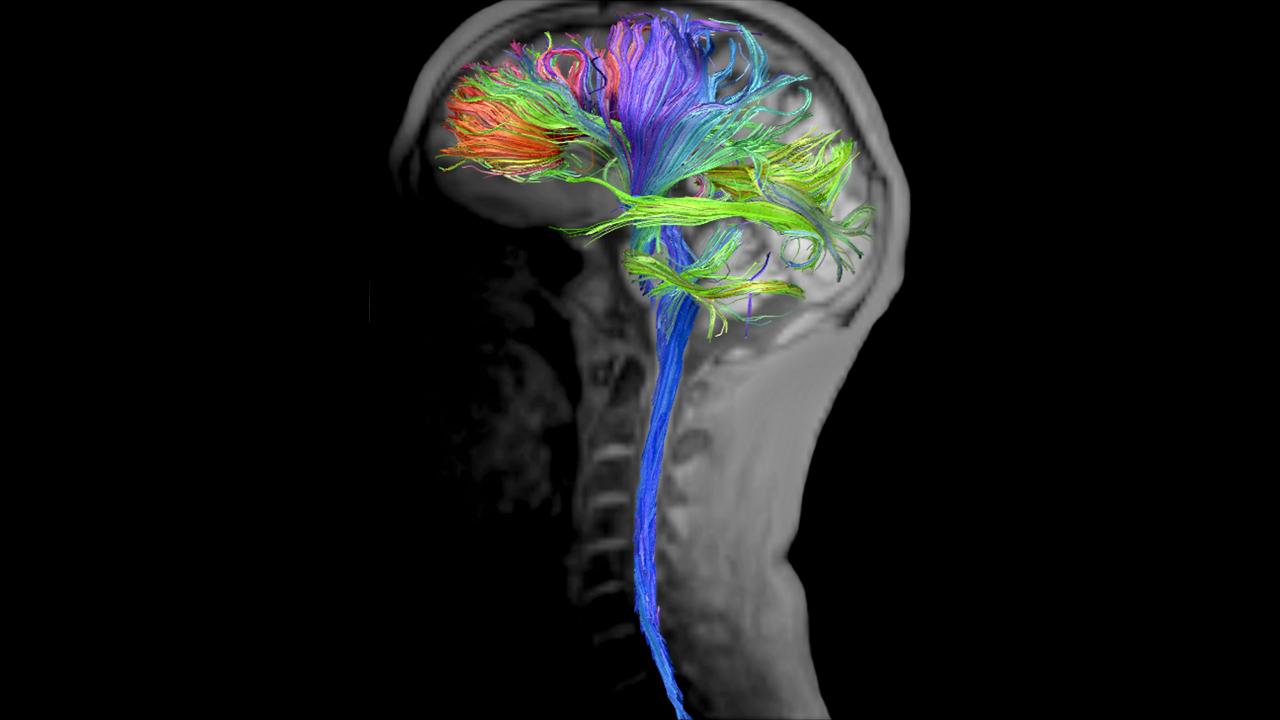







- Clinical applications in neurology, oncology and pediatric2 imaging.
- Particularly useful in the evaluation of smaller lesions.
- RESOLVE provides outstanding balance between imaging speed and quality compared to other diffusion-weighted imaging sequences.
- Further enhancement of capabilities and speed with SMS acceleration.
Χαρακτηριστικά και Οφέλη
Outstanding DWI diagnostic performance with RESOLVE
The clinical impact of RESOLVE has been shown in a variety of examinations, including the brain, skull base, spine, breast, prostate, pelvis and rectum. Compared to alternative methods RESOLVE brings the best balance of imaging speed and quality.
Benefits
- High-quality, high-resolution DWI and DTI
- Reduced susceptibility and blurring artifacts
- Insensitivity to motion-induced phase errors
- Reduced SAR in comparison to TSE-based methods
- iPAT compatible for faster scans and further reduced distortions
- SMS acceleration for additional acquisition time reduction of up to 60%

RESOLVE uses the same diffusion preparation as single-shot EPI, however, the k-space trajectory is divided into multiple segments in the readout direction, which allows for a TE and and an encoding-time reduction increasing image quality.
- Readout-segmented, multi-shot EPI for reduced TE and encoding time
- Motion correction with 2D phase navigator and real-time image reacqusition for unusable data

High Resolution Diffusion-Weighted Imaging Using Readout-Segmented Echo-Planar Imaging, Parallel Imaging and a Two-Dimensional Navigator-Based Reacquisition.
(Porter & Heidemann)
Additional information
The diffusion rate of water molecules in different tissues correlates with their physiological state, and may be altered in disease. Diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) enables visualization and measurement of abnormal diffusivity, revealing lesions which may go unnoticed with conventional anatomical MR or CT imaging alone. The practical clinical value of DWI is well established. Despite some challenges in certain body regions, particularly at higher field strengths, DWI is now broadly used in clinical routine.
Κλινική Χρήση
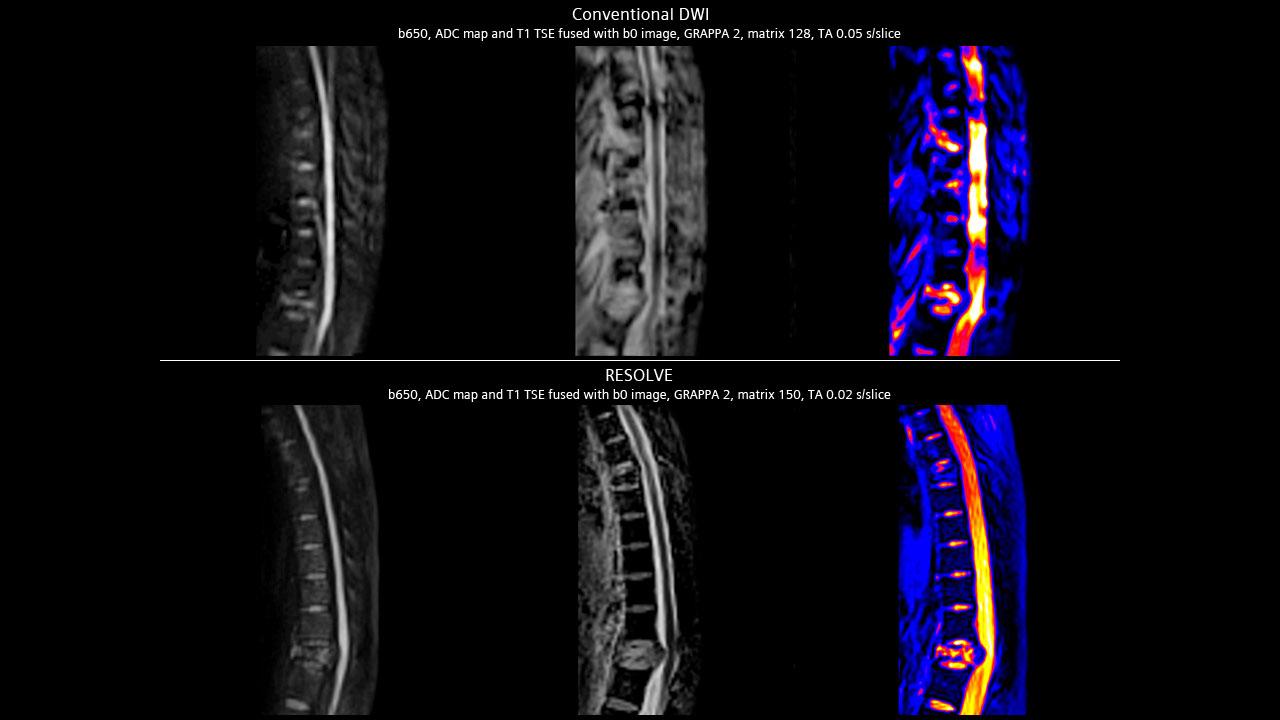




Neuroimaging
Left: Hippocampal lesion (Image: Ebara Hospital, Tokyo, Japan - MAGNETOM Trio, A Tim System)
Right: Spine Post accident, TH6 and TH12 fracture (Image: Singapore General Hospital, Singapore - MAGNETOM Avanto)

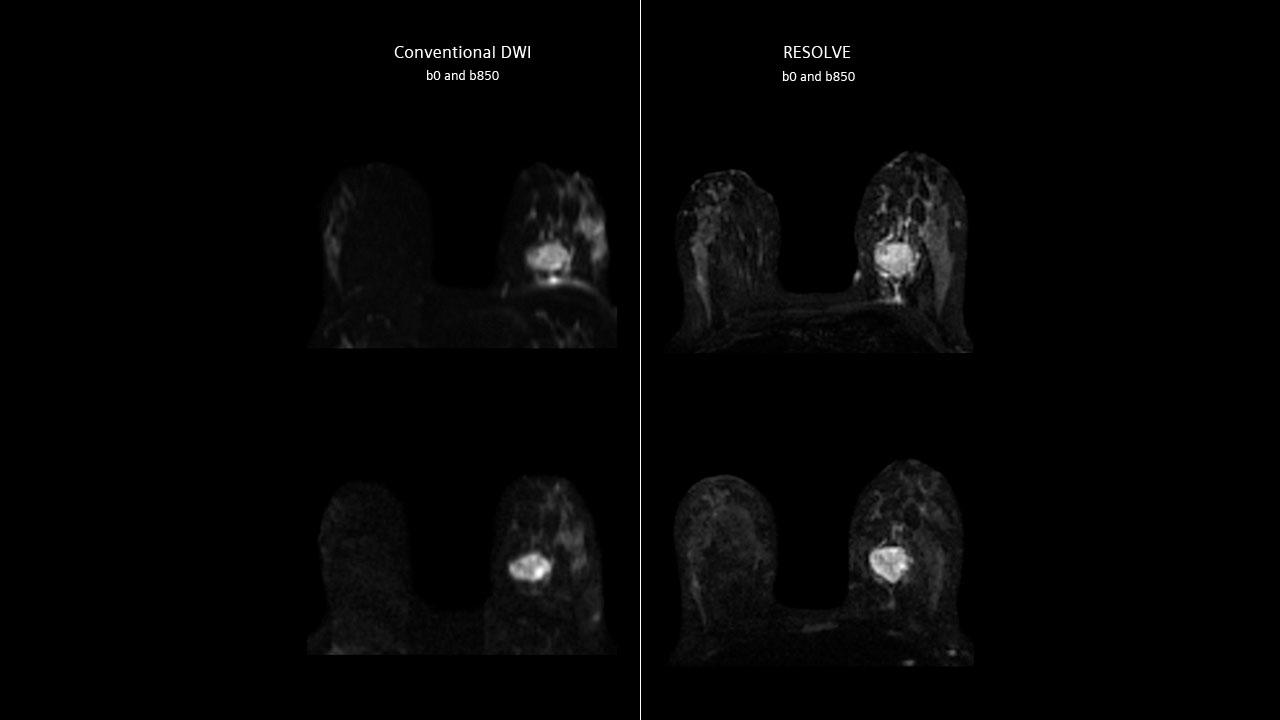



Body imaging
Left: Breast Carcinoma (Image: AKH, Vienna, Austria - MAGNETOM Trio, A Tim System)
Right: Prostate Carcinoma (Image: National University Hospital, Singapore - MAGNETOM Skyra)

Pediatric imaging1
Drop metastases to the spine 2 year old female (Image: Children's Healthcare of Atlanta at Scottish Rite, Atlanta, USA - MAGNETOM Avanto)
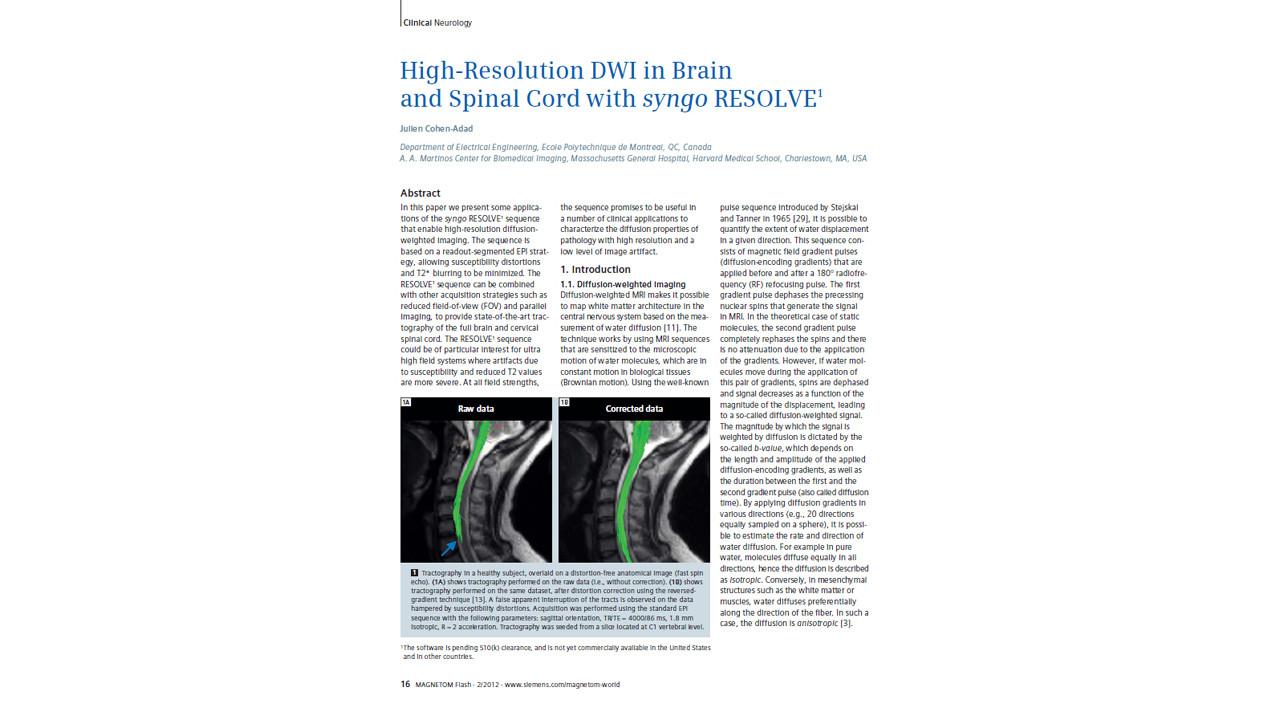
High-Resolution DWI in Brain and Spinal Cord with RESOLVE (Cohen-Adad)
“At all field strengths, the sequence promises to be useful in a number of clinical applications to characterize the diffusion properties of pathology with high resolution and a low level of image artifact."2

Echo Planar Diffusion-Weighted Imaging: Possibilities and Considerations with 12- and 32-Channel Head Coils. (Morelli, et al)
“The utility of single-shot (ss) and an approach to readout-segmented (rs) echo planar imaging (EPI) are examined. Substantial image quality improvements are found with rs-EPI.”

Benign versus metastatic vertebral compression fractures: combined diffusion-weighted MRI and MR spectroscopy aids differentiation. (Rumpel, et al)
“Diffusion-weighted read-out-segmented echoplanar imaging improves spinal image quality.”

Anatomical details of the brainstem and cranial nerves visualized by high resolution readout-segmented multi-shot echo-planar diffusion-weighted images using unidirectional MPG at 3T. (Nagawa, et al)
“DWI by rs-EPI was significantly better than DWI by single-shot EPI for visualizing the medial longitudinal fasciculus, lateral lemniscus, corticospinal tract, and seventh/eighth cranial nerves and offered significantly less distortion of the brainstem.”

Drop metastases to the pediatric spine revealed with diffusion-weighted MR imaging. (Hayes, et al)
“DWI of the spine has not been clinically useful in children because of susceptibility artifacts and lack of spatial resolution. A new technique, readout-segmented echo planar imaging (EPI), has improved these images, allowing for identification of hypercellular drop metastases.”

Readout-segmented echo-planar imaging improves the diagnostic performance of diffusion-weighted MR breast examinations at 3.0 T (Bogner, et al)
“Readout-segmented echo-planar imaging reached a higher diagnostic accuracy for the differentiation of benign and malignant breast lesions.”
General Requirements
System
- MAGNETOM Amira
- MAGNETOM Vida
- MAGNETOM Verio
- MAGNETOM Skyra eco
- MAGNETOM Spectra
- MAGNETOM ESSENZA
- MAGNETOM Skyra
- MAGNETOM Aera
- MAGNETOM Prisma
- MAGNETOM Altea
- MAGNETOM Lumina
Minimum Software Version
syngo MR D13 or D14
syngo MR XA11B for the availability of SMS acceleration1
Other
Also available for:
MAGNETOM Prismafit
MAGNETOM Skyrafit
MAGNETOM Avanto Tim+Dot
MAGNETOM Avantofit
MAGNETOM ESSENZA Tim+Dot
MAGNETOM Verio Tim+Dot
Please Note: Additional technical pre-requisites may apply. Upon receiving your request, your local Siemens representative will clarify whether your system meets the requirements.