- Home
- Solutions informatiques et logicielles
- Artificial Intelligence
- AI campaign
- Automatic contouring with Organs RT
Automatic contouring with Organs RT
Organs RT automatically contours several organs at risk. This input can be used for further processing in a treatment planning system. This enables physicians to free up resources for other time-consuming tasks and drives standardization across different individuals and institutions.
Available
in syngo.via and AI-Rad Companion
The need for organs at risk contouring in radiation therapy
The process of contouring all organs at risk is a tedious and time consuming process. RT professionals spend a significant amount of time contouring manually on each slice of the CT dataset. Manual contouring can also lack consistency, because contours can differ from user to user.
While the task of organs at risk contouring is necessary, it’s a task that can be automated to help deliver consistency across users and patient encounters.
The predicted increase in cancer cases worldwide will lead to a growing number of patients who need to be treated with radiation therapy.
Automating these routine tasks can help free up staff to focus on more value-adding work.
AI-powered contouring support for organs at risk
Organs RT is an AI-based solution that provides radiation therapists with automatic contouring of organs at risk, which is input to their radiation therapy planning. The images acquired at the CT scanner are sent to Organs RT to be processed, and then the RT struct (DICOM) results can be pushed directly to the treatment planning system or first assessed in the Organs RT interface.
Organs RT provides organs at risk contours using deep-learning (AI) algorithms for various body regions, including head and neck, thorax, abdomen, and pelvis. It also supports the use of organ template configurations that can be aligned with institutional protocols; this may save time and improve standardization in clinical workflows.

Generated OAR contours based on CT images for various body region (head, neck, thorax, abdomen and pelvis)
AI behind automatic contouring of OARs
The automatic process of contouring OARs relies on a deep learning based model which consists of a two steps approach as seen in Figure 1. In the first step, the target organ region in the optimal input image is extracted using a trained Deep Reinforcement Learning network (DRL). The result is a cropped image of the target organ region. In the second step, the cropped image is used as input to create the contours. This step is based on a DI2IN. The DI2IN was trained to its optimal performance in the Siemens Healthineers AI environment. The DRL algorithm also has the ability to detect multiple target regions.

Figure 1 : Two step algorithm for DL-based contouring.
What are the key benefits?
By leveraging Artificial Intelligence (AI) to generate OAR contouring, AI-Rad Companion Organs RT, enables high quality OAR contouring to drive standardization with AI-powered algorithms. These benefits can potentially free up staff to spend more time on other tasks and help to simplify radiotherapy planning workflow.
Deployment model
Organs RT can be seamlessly integrated in your daily workflow using either cloud-based approach with AI-Rad Companion or on-site deployment with Syngo.via. This flexibility enables the institution to select the option that best fits to their privacy requirements and desired workflow.
Clinical examples
Discover how AI-Rad Companion supports you as a full-time radiology expert
The AI-Rad Companion Organs RT automatically contours the organs at risk with the support of deep learning algorithms. It may reduce unwarranted variations with high-quality contours that approach the level of consensus-based contours.
Courtesy
of Leopoldina-Krankenhaus der Stadt Schweinfurt GmbH, Schweinfurt, Germany


CT scan of the head with AI-Rad Companion Organs RT generated contouring of organs at risk.
Courtesy of Leopoldina-Krankenhaus der Stadt Schweinfurt GmbH, Schweinfurt, Germany
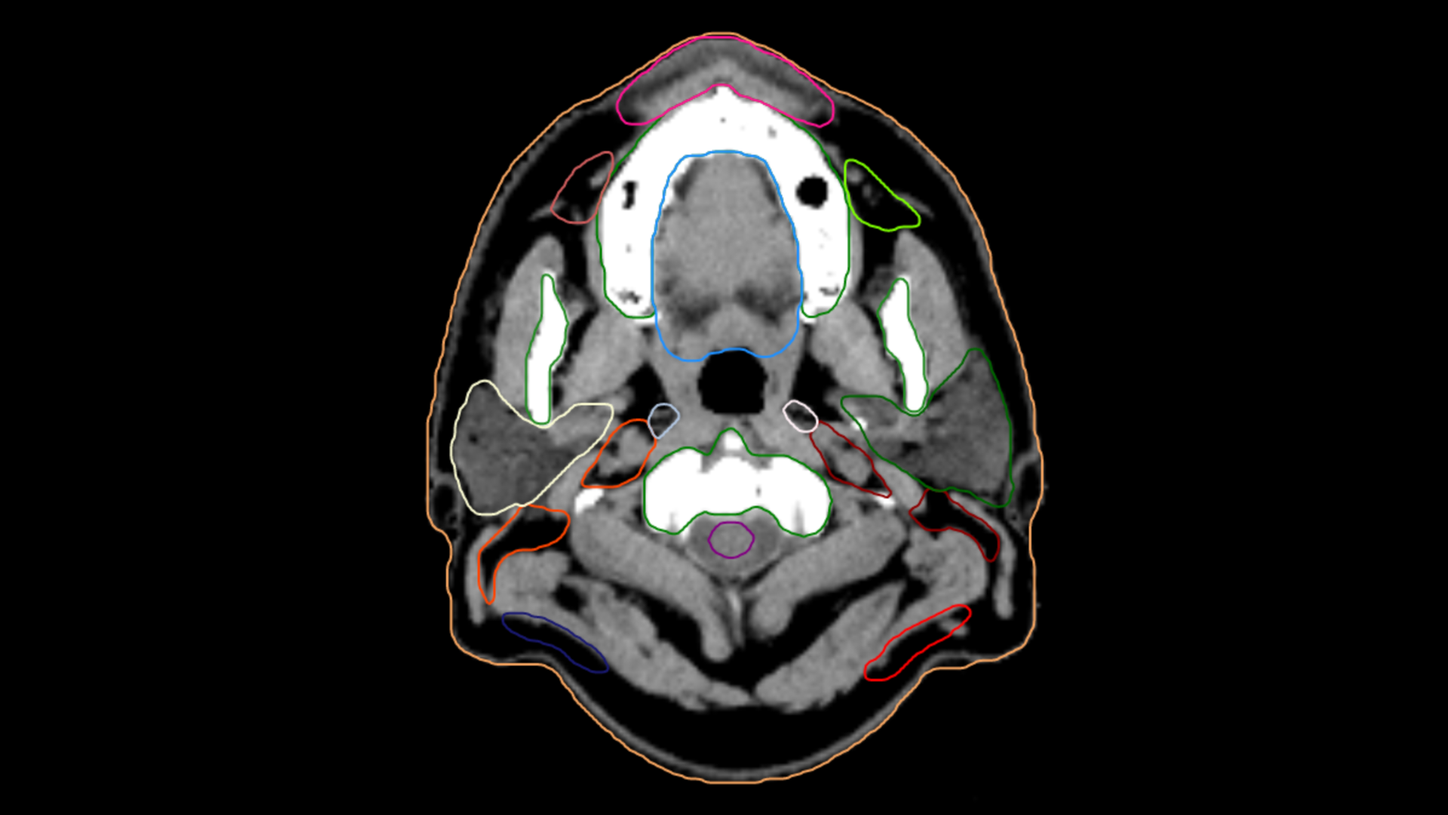
CT Scan of the head and neck with AI-Rad Companion Organs RT generated contours of different organs, including the lymph nodes (VA40).
Courtesy
of Leopoldina-Krankenhaus der Stadt Schweinfurt GmbH, Schweinfurt, Germany
The AI-Rad Companion Organs RT automatically contours the organs at risk with the support of deep learning algorithms. It may reduce unwarranted variations with high-quality contours that approach the level of consensus-based contours.
Courtesy
of Leopoldina-Krankenhaus der Stadt Schweinfurt GmbH, Schweinfurt, Germany


CT scan of the head with AI-Rad Companion Organs RT generated contouring of organs at risk.
Courtesy of Leopoldina-Krankenhaus der Stadt Schweinfurt GmbH, Schweinfurt, Germany

CT Scan of the head and neck with AI-Rad Companion Organs RT generated contours of different organs, including the lymph nodes (VA40).
Courtesy
of Leopoldina-Krankenhaus der Stadt Schweinfurt GmbH, Schweinfurt, Germany
The AI-Rad Companion Organs RT automatically contours the organs at risk with the support of deep learning algorithms. It may reduce unwarranted variations with high-quality contours that approach the level of consensus-based contours.
Courtesy
of Leopoldina-Krankenhaus der Stadt Schweinfurt GmbH, Schweinfurt, Germany



Customer experiences
“The use of AI-Rad Companion Organs RT makes our life easier. Especially the contouring of organs in the upper abdomen, leads to a noteworthy reduction of turnaround time.”

Dr. Alexandros Papachristofilou University Hospital Basel, Switzerland
Contact
See the other topics here