- Home
- Digital Solutions & Automation
- AI-Rad Companion

AI-Rad CompanionProviding multi-modality imaging decision support

Experience the AI-Rad Companion Trial Light
The power of AI is just a few clicks away.
With AI-Rad Companion Trial Light1 you can easily experience the quality of our algorithms – directly via your browser and without any installation effort.
Overview
The AI-Rad Companion, our family of AI-powered, augmented workflow solutions, helps you to reduce the burden of basic repetitive tasks and may increase your diagnostic precision when interpreting medical images.
Its solutions provide automatic post-processing of imaging datasets through our AI-powered algorithms. The automation of routine workflows with repetitive tasks and high case volumes helps you to ease your daily workflow – so that you can focus on more critical issues.
Up-to-date algorithms and scalable offerings
Our state-of-the-art algorithms will be automatically distributed to you as a user as soon as they are officially released and made available. Once the images are post-processed by the AI-Rad Companion, it supports your interpretation of the data by automatically providing results of its analysis to you for review, confirmation and possible inclusion in the final report or care pathway – to raise your precision and ensure high quality outcome in diagnostic decision-making.
All our AI-Rad Companion extensions are deployed via the teamplay digital health platform. This approach eases regular updates as well as upgrade processes and facilitates the integration of new offerings into the existing IT environment.
The AI-Rad Companion family is growing

Clinical Outcomes
AI-Rad Companion may help you to increase precision and speed up your workflow
We developed the AI-Rad Companion to help you cope with a growing workload. With its deep learning algorithms, AI-Rad Companion automatically highlights abnormalities, segments anatomies, and compares results to reference values.
Discover how AI-Rad Companion supports you as a full-time radiology expert
Brain MR
03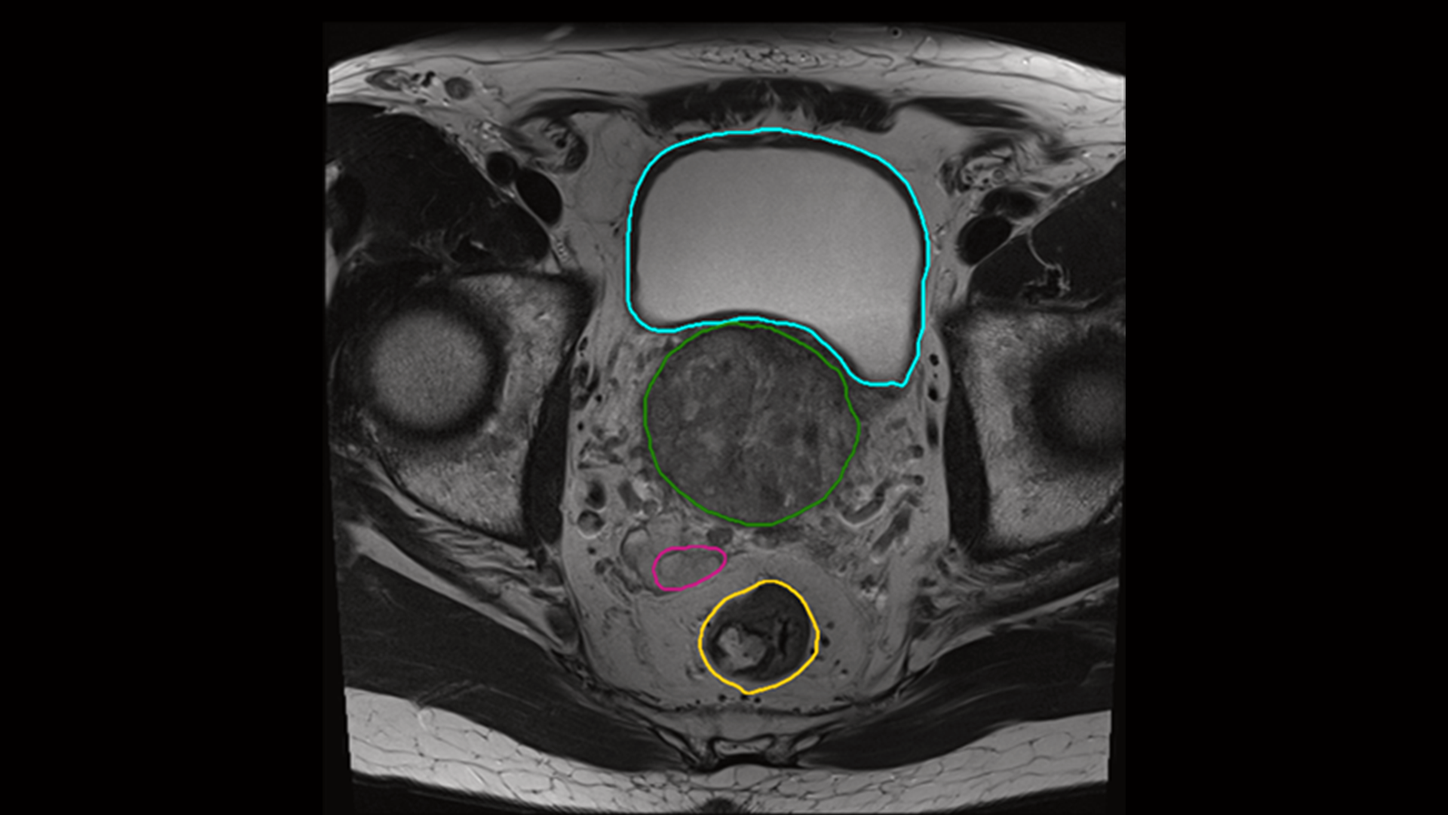
AI-Rad Companion Organs RT now also supports MR-based organs-at-risk for male pelvis4.
Courtesy of Leopoldina-Krankenhaus der Stadt Schweinfurt GmbH, Schweinfurt, Germany


The AI-Rad Companion Chest CT detects and highlights lung nodules. After segmentation of the lung nodules, the volume, maximum 2D diameter, maximum 3D diameter and tumor burden are automatically calculated.
Courtesy of Klinikum Nürnberg, Nuremberg, Germany

Cinematic Rendering adds clarity to the location of a detected lung nodule. The visualization makes it easy for the referring physician to get a clear picture of the nodule location within the lung.
Courtesy of Klinikum Nürnberg, Nuremberg, Germany

The AI-Rad Companion Chest CT automatically recognizes coronary calcium, calculates its volume, and creates an enhanced clinical image including quantification of the heart volume. This additional information about a cardiac condition is valuable clinical knowledge to a routine Chest CT study.
Courtesy of Klinikum Nürnberg, Nuremberg, Germany

This 3D overview of the thoracic aorta has been automatically created by the AI-Rad Companion Chest CT. It includes the measurement of relevant diameters, based on medical guidelines, and detected anatomical landmarks. This clearly shows how the AI-Rad Companion Chest CT can support the increase of accuracy of your reporting.

The AI-Rad Companion Chest CT has automatically created this measurement of the aorta based on a non-contrast enhanced CT image.
Courtesy of Klinikum Nürnberg, Nuremberg, Germany

On this image you can see how the height of the vertebrae bodies is measured and compared. The AI-Rad Companion Chest CT automatically processes these measurements and marks abnormalities with easy-to-understand color-coding. Deviations are highlighted, while bone density is reported in Hounsfield Units.
Courtesy of Klinikum Nürnberg, Nuremberg, Germany

The new functionality Pulmonary Density automatically identifies and quantifies hyperdense areas of the lung using non-contrast enhanced chest CT’s. The opacity score helps to assess the percentage of affected lung tissue.

Certain parts of the pulmonary density functionality1 of AI-Rad Companion Chest CT were used in the prototype Siemens Healthineers offered to fight COVID-19, to analyze ground-glass opacities and consolidations. High opacity abnormalities were shown to correlate with lungs of COVID-19 patients.
For this sub mSv CT examination the Tin Filter technology is used.
kV: Sn130 kV, Q. ref mAs: 40 mAs, CTDIvol: 1,38 mGy DLP: 51
Eff. Dose: 0,86 mSv
Courtesy of CHR East Belgium, Verviers, Belgium

A 360° VRT overview visualizes the affected areas.
Courtesy of CHR East Belgium, Verviers, Belgium
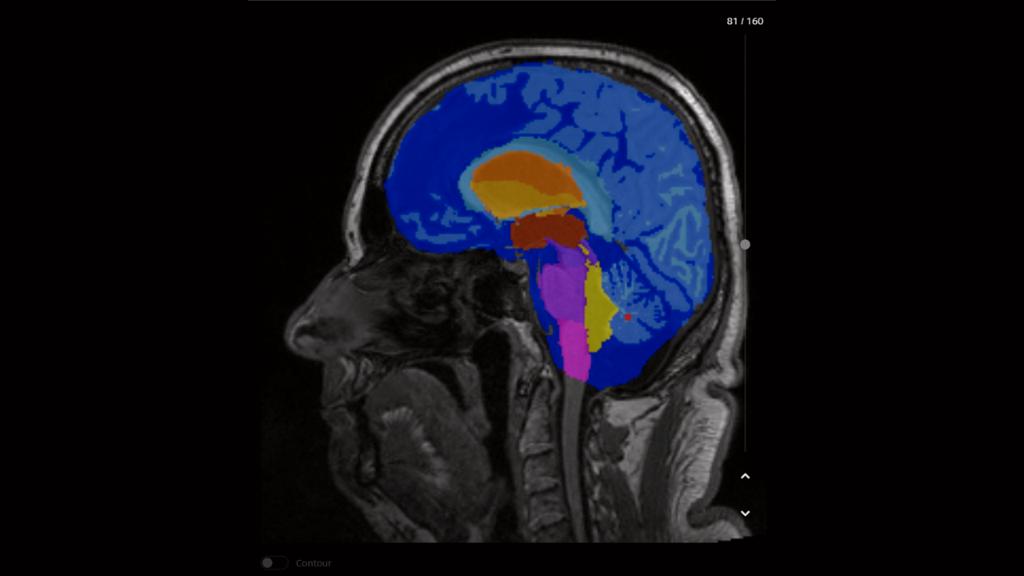
AI-Rad Companion performs an automatic segmentation of the different brain structures and provides individual volumetric analysis.
Courtesy of CHUV, Lausanne, Switzerland, Case 2aaaa1366

AI-Rad Companion compares the different volumes to a normative database and automatically generates a highlighted deviation map.
Courtesy of University Hospital Mannheim, Germany

AI-Rad Companion automatically generates a report with all volumetric analyses listed, deviations from the normative database are marked. All results can be transferred to PACS based on the configuration.
Courtesy of Centre d'imagerie diagnostique, Lausanne, Switzerland, Case 2aaaa1366

AI-Rad Companion Prostate MR performs an automated segmentation of the prostate gland, marks the organ’s outer contour and conducts volume calculation of the prostate gland. When the PSA value is known, it calculates the PSA density. The segmentation results can be exported as “burnt-in” contours in a Radiotherapy Structure Sets (RTSS) format which is then used by urologists in TRUS (Transrectal Ultrasound)-guided biopsies.
Courtesy Radiomedicum, Bad Nauheim, Germany

The algorithm automatically detects, segments, quantifies and classifies suspicious prostate lesions and provides this information along with a lesion score and visualization of their localization on a pictogram. The radiologist can manually adjust segmentations as well as the lesion, lesion score and localization and diameter of the lesion.
Courtesy Radiomedicum, Bad Nauheim, Germany


PA chest X-ray of a patient showing an AI-Rad Companion Chest X-ray lung lesion finding in the right lung and
atelectasis in the left lung
Courtesy of MVZ Prof. Dr. Uhlenbrock & Partner GmbH, Dortmund, Germany

PA chest X-ray of a patient showing AI-Rad Companion Chest X-ray findings of two lung lesions in the left lung and the consolidation in the right lung.
Courtesy of MVZ Prof. Dr. Uhlenbrock & Partner GmbH, Dortmund, Germany


CT scan of the head with AI-Rad Companion Organs RT generated contouring of organs at risk.
Courtesy of Leopoldina-Krankenhaus der Stadt Schweinfurt GmbH, Schweinfurt, Germany
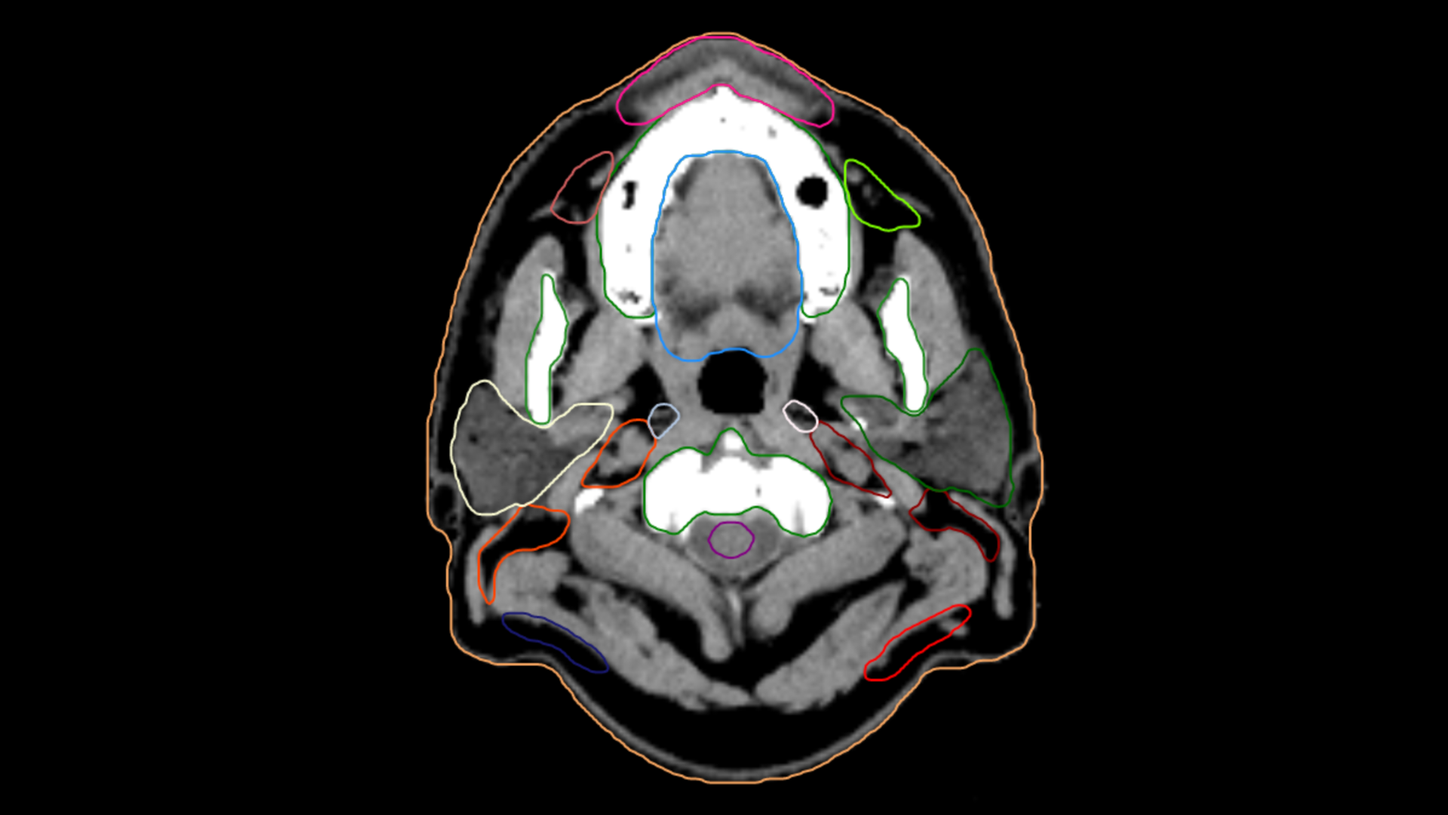
CT Scan of the head and neck with AI-Rad Companion Organs RT generated contours of different organs, including the lymph nodes (VA40).
Courtesy
of Leopoldina-Krankenhaus der Stadt Schweinfurt GmbH, Schweinfurt, Germany
The AI-Rad Companion Organs RT automatically contours the organs at risk with the support of deep learning algorithms. It may reduce unwarranted variations with high-quality contours that approach the level of consensus-based contours.
Courtesy
of Leopoldina-Krankenhaus der Stadt Schweinfurt GmbH, Schweinfurt, Germany

AI-Rad Companion Organs RT now also supports MR-based organs-at-risk for male pelvis4.
Courtesy of Leopoldina-Krankenhaus der Stadt Schweinfurt GmbH, Schweinfurt, Germany


The AI-Rad Companion Chest CT detects and highlights lung nodules. After segmentation of the lung nodules, the volume, maximum 2D diameter, maximum 3D diameter and tumor burden are automatically calculated.
Courtesy of Klinikum Nürnberg, Nuremberg, Germany

Cinematic Rendering adds clarity to the location of a detected lung nodule. The visualization makes it easy for the referring physician to get a clear picture of the nodule location within the lung.
Courtesy of Klinikum Nürnberg, Nuremberg, Germany

The AI-Rad Companion Chest CT automatically recognizes coronary calcium, calculates its volume, and creates an enhanced clinical image including quantification of the heart volume. This additional information about a cardiac condition is valuable clinical knowledge to a routine Chest CT study.
Courtesy of Klinikum Nürnberg, Nuremberg, Germany

This 3D overview of the thoracic aorta has been automatically created by the AI-Rad Companion Chest CT. It includes the measurement of relevant diameters, based on medical guidelines, and detected anatomical landmarks. This clearly shows how the AI-Rad Companion Chest CT can support the increase of accuracy of your reporting.

The AI-Rad Companion Chest CT has automatically created this measurement of the aorta based on a non-contrast enhanced CT image.
Courtesy of Klinikum Nürnberg, Nuremberg, Germany

On this image you can see how the height of the vertebrae bodies is measured and compared. The AI-Rad Companion Chest CT automatically processes these measurements and marks abnormalities with easy-to-understand color-coding. Deviations are highlighted, while bone density is reported in Hounsfield Units.
Courtesy of Klinikum Nürnberg, Nuremberg, Germany

The new functionality Pulmonary Density automatically identifies and quantifies hyperdense areas of the lung using non-contrast enhanced chest CT’s. The opacity score helps to assess the percentage of affected lung tissue.

Certain parts of the pulmonary density functionality1 of AI-Rad Companion Chest CT were used in the prototype Siemens Healthineers offered to fight COVID-19, to analyze ground-glass opacities and consolidations. High opacity abnormalities were shown to correlate with lungs of COVID-19 patients.
For this sub mSv CT examination the Tin Filter technology is used.
kV: Sn130 kV, Q. ref mAs: 40 mAs, CTDIvol: 1,38 mGy DLP: 51
Eff. Dose: 0,86 mSv
Courtesy of CHR East Belgium, Verviers, Belgium

A 360° VRT overview visualizes the affected areas.
Courtesy of CHR East Belgium, Verviers, Belgium

AI-Rad Companion performs an automatic segmentation of the different brain structures and provides individual volumetric analysis.
Courtesy of CHUV, Lausanne, Switzerland, Case 2aaaa1366


AI-Rad Companion compares the different volumes to a normative database and automatically generates a highlighted deviation map.
Courtesy of University Hospital Mannheim, Germany

AI-Rad Companion automatically generates a report with all volumetric analyses listed, deviations from the normative database are marked. All results can be transferred to PACS based on the configuration.
Courtesy of Centre d'imagerie diagnostique, Lausanne, Switzerland, Case 2aaaa1366

AI-Rad Companion Prostate MR performs an automated segmentation of the prostate gland, marks the organ’s outer contour and conducts volume calculation of the prostate gland. When the PSA value is known, it calculates the PSA density. The segmentation results can be exported as “burnt-in” contours in a Radiotherapy Structure Sets (RTSS) format which is then used by urologists in TRUS (Transrectal Ultrasound)-guided biopsies.
Courtesy Radiomedicum, Bad Nauheim, Germany

The algorithm automatically detects, segments, quantifies and classifies suspicious prostate lesions and provides this information along with a lesion score and visualization of their localization on a pictogram. The radiologist can manually adjust segmentations as well as the lesion, lesion score and localization and diameter of the lesion.
Courtesy Radiomedicum, Bad Nauheim, Germany


PA chest X-ray of a patient showing an AI-Rad Companion Chest X-ray lung lesion finding in the right lung and
atelectasis in the left lung
Courtesy of MVZ Prof. Dr. Uhlenbrock & Partner GmbH, Dortmund, Germany

PA chest X-ray of a patient showing AI-Rad Companion Chest X-ray findings of two lung lesions in the left lung and the consolidation in the right lung.
Courtesy of MVZ Prof. Dr. Uhlenbrock & Partner GmbH, Dortmund, Germany


CT scan of the head with AI-Rad Companion Organs RT generated contouring of organs at risk.
Courtesy of Leopoldina-Krankenhaus der Stadt Schweinfurt GmbH, Schweinfurt, Germany

CT Scan of the head and neck with AI-Rad Companion Organs RT generated contours of different organs, including the lymph nodes (VA40).
Courtesy
of Leopoldina-Krankenhaus der Stadt Schweinfurt GmbH, Schweinfurt, Germany
The AI-Rad Companion Organs RT automatically contours the organs at risk with the support of deep learning algorithms. It may reduce unwarranted variations with high-quality contours that approach the level of consensus-based contours.
Courtesy
of Leopoldina-Krankenhaus der Stadt Schweinfurt GmbH, Schweinfurt, Germany

AI-Rad Companion Organs RT now also supports MR-based organs-at-risk for male pelvis4.
Courtesy of Leopoldina-Krankenhaus der Stadt Schweinfurt GmbH, Schweinfurt, Germany























Integration in clinical routine
AI-Rad Companion can be fully integrated into the image interpretation workflow and helps you to handle your daily workload with greater ease – drive productivity with seamless integration in the reading and reporting workflow including automated measurements and DICOM structured reports while every workflow step remains under control to enable evidence based decisions. The AI-Rad Companion with Notifier enables radiologists to review AI results independent of any limitations of their current PACS system. AI-Rad Companion offers results in different data formats which enable advanced integration options, e.g. receive AI results directly in your reporting templates.

Smooth integration of artificial intelligence into the radiology environment
Download our real-world clinical scenario and read how the AI-Rad Companion Chest CT is being used at Diagnostikum Linz, Austria5 in order to assess the thoracic aorta. Learn from the expert how AI-Rad Companion Chest CT does have a positive impact on reading and reporting, but also on patient care and workload improvements for radiographers.
“AI-supported software gives us more confidence in cancer care”
In Zagreb, a specialist hospital with 100 employees gives cancer patients from all over the region a chance of survival. AI solutions provide valuable support.
Evidence
Dr. Karsten Ridder
Dortmund Healthcare Center Prof. Dr. Uhlenbrock and Partner,
Germany
ChestRad Perth
Dr Conor Murray - CEO and Lead Radiologist
Prof. Rozemarijn Vliegenthart
Data Science Center in Health,
Universitair Medisch Centrum Groningen, The Netherlands
Prof. Dr. Ronan Killeen
Consultant Neuroradiologist and Nuclear Medicine
Physician, National Delegate European Association of
Nuclear Medicine at Saint Vincent' s University Hospital
Dublin, Ireland
Dr. John Sheehan
Clinical Director at Blackrock Health, Ireland
Dr. Firas Mourtada
Sidney Kimmel Comprehensive Cancer Center at Jefferson,
USA
Dr. Firas Mourtada
Sidney Kimmel Comprehensive Cancer Center at Jefferson,
USA
Benefit: Accuracy
Dr. Firas Mourtada
Sidney Kimmel Comprehensive Cancer Center at Jefferson,
USA
Benefit: Consistency
Dr. Firas Mourtada
Sidney Kimmel Comprehensive Cancer Center at Jefferson,
USA
Benefit: Time Savings
Dr. Firas Mourtada
Sidney Kimmel Comprehensive Cancer Center at Jefferson,
USA
Benefit: User-Friendly
Dr. Jurgen Fuetterer
University of Twente, The Netherlands
Dr. Karsten Ridder
Dortmund Healthcare Center Prof. Dr. Uhlenbrock and Partner,
Germany
ChestRad Perth
Dr Conor Murray - CEO and Lead Radiologist
Prof. Rozemarijn Vliegenthart
Data Science Center in Health,
Universitair Medisch Centrum Groningen, The Netherlands
Prof. Dr. Ronan Killeen
Consultant Neuroradiologist and Nuclear Medicine
Physician, National Delegate European Association of
Nuclear Medicine at Saint Vincent' s University Hospital
Dublin, Ireland
Dr. John Sheehan
Clinical Director at Blackrock Health, Ireland
Dr. Firas Mourtada
Sidney Kimmel Comprehensive Cancer Center at Jefferson,
USA
Dr. Firas Mourtada
Sidney Kimmel Comprehensive Cancer Center at Jefferson,
USA
Benefit: Accuracy
Dr. Firas Mourtada
Sidney Kimmel Comprehensive Cancer Center at Jefferson,
USA
Benefit: Consistency
Dr. Firas Mourtada
Sidney Kimmel Comprehensive Cancer Center at Jefferson,
USA
Benefit: Time Savings
Dr. Firas Mourtada
Sidney Kimmel Comprehensive Cancer Center at Jefferson,
USA
Benefit: User-Friendly
Dr. Jurgen Fuetterer
University of Twente, The Netherlands
Dr. Karsten Ridder
Dortmund Healthcare Center Prof. Dr. Uhlenbrock and Partner,
Germany